Figure 3.
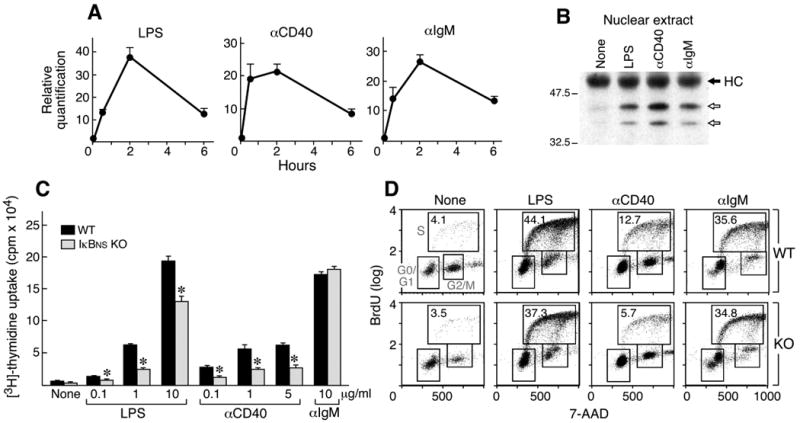
Induction of IκBNS and proliferation of IκBNS KO and WT B cells in response to LPS, anti-IgM and anti-CD40. A) RNA was isolated from WT B cells 0, 0.5, 2 and 6 hours after stimulation by the indicated mitogens and examined for IκBNS expression by real-time PCR. B) Splenic B cells (CD43-) were treated for 2 hours with the indicated reagent or left untreated (None). Nuclear lysates (50μg) were immunoprecipitated using anti-IκBNS antisera. After transfer to PVDF membranes, IκBNS was identified using an anti-IκBNS mAb for Western blotting. Arrows indicate two isoforms. HC indicates the heavy chain of the immunoprecipitating IgG. C) Splenic B cells (CD43-) were incubated for 48 hours in the presence of media only (None) or the indicated reagents (0.1, 1 or 10 μg/ml LPS, 0.1, 1 or 5 μg/ml anti-CD40, 10 μg/ml anti-IgM). Proliferation was measured by 3H-thymidine incorporation. *p<0.01 D) BrdU cell cycle analysis. Cells were pulsed with BrdU, then stained with anti-BrdU antibody and 7-AAD. Percentages of BrdU-positive S phase cells are indicated. Two independent experiments were performed and similar results obtained.
