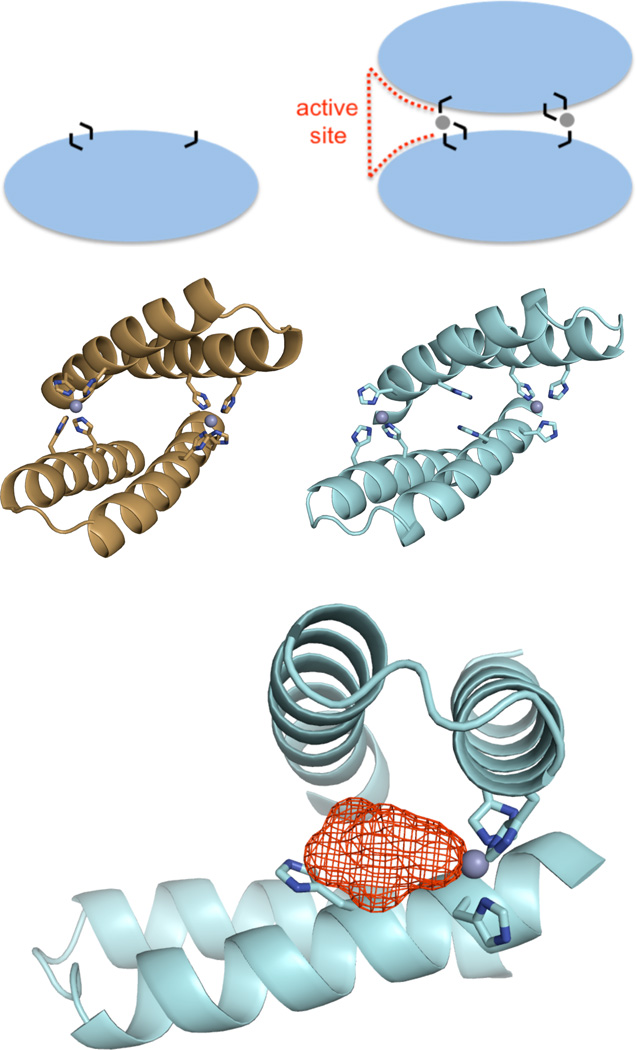
Figure 1.
A metal-mediated protein interface as a minimalist route to a new active site. A) A zinc-mediated protein homodimer is a simple recipe for an active site: dimer interfaces naturally contain peripheral clefts (red dashes), metal binding can promote protein interactions, and metal is an effective catalytic motif. Black lines represent histidines, and gray spheres represent zinc ions. B) The computational predictive model of MID1-zinc. Design of MID1-zinc was structurally motivated, the goal was to engineer a de novo zinc-mediated protein-protein interaction. C) Crystallographyically, we observed only three of the four histidines actually participated in zinc coordination. D) Because we observed a cleft (red mesh) and an open zinc coordination site at the MID1-zinc interface, we investigated MID1-zinc as a primitive enzyme.