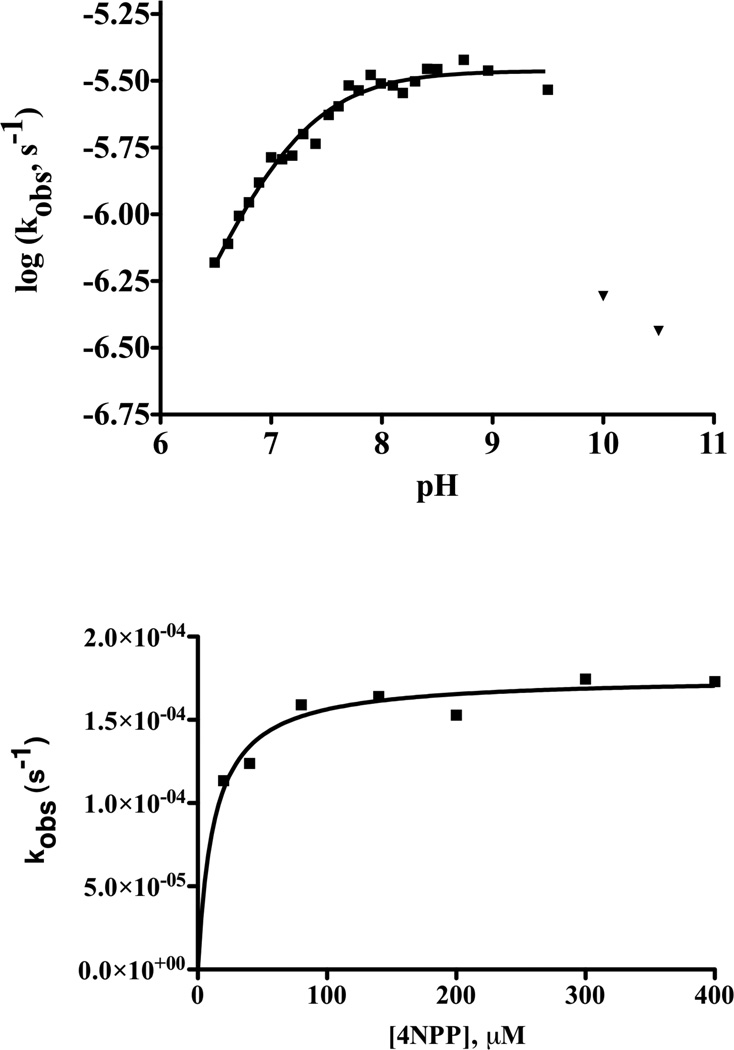
Figure 6.
MID1-zinc catalyses 4NPP hydrolysis. a) pH rate profile for the MID1-zinc catalyzed hydrolysis of 4-nitrophenyl phosphate determined by monitoring product formation at 400 nm. The data from pH 6.5 to 9.5 (squares) were fit to Equation 2, giving a kcat = (3.5 ± 0.09) × 10−6 s−1 and a pKa = 7.1 ± 0.03. The data obtained at pH > 9.5 (inverted triangles) indicate a slope of < −1 suggesting catalyst instability at high pH. The high pH points were excluded from the NLLSQ fit of the data. Reaction conditions were: 2.5 µM MID1-zinc, 40 µM 4NPP, 40 mM buffer (HEPES for pH 6.5 – 8.5, or potassium hydrogen carbonate for pH > 8.5), 50 mM NaCl, and 37°C. b) Plot of kobs versus [4NPP] for MID1-zinc catalyzed hydrolysis at pH 8.5 and 37°C. A fit of the data to a standard binding equation gives kcat = (1.8 ± 0.05) × 10−4 s−1 and KM = (12 ± 2) µM.