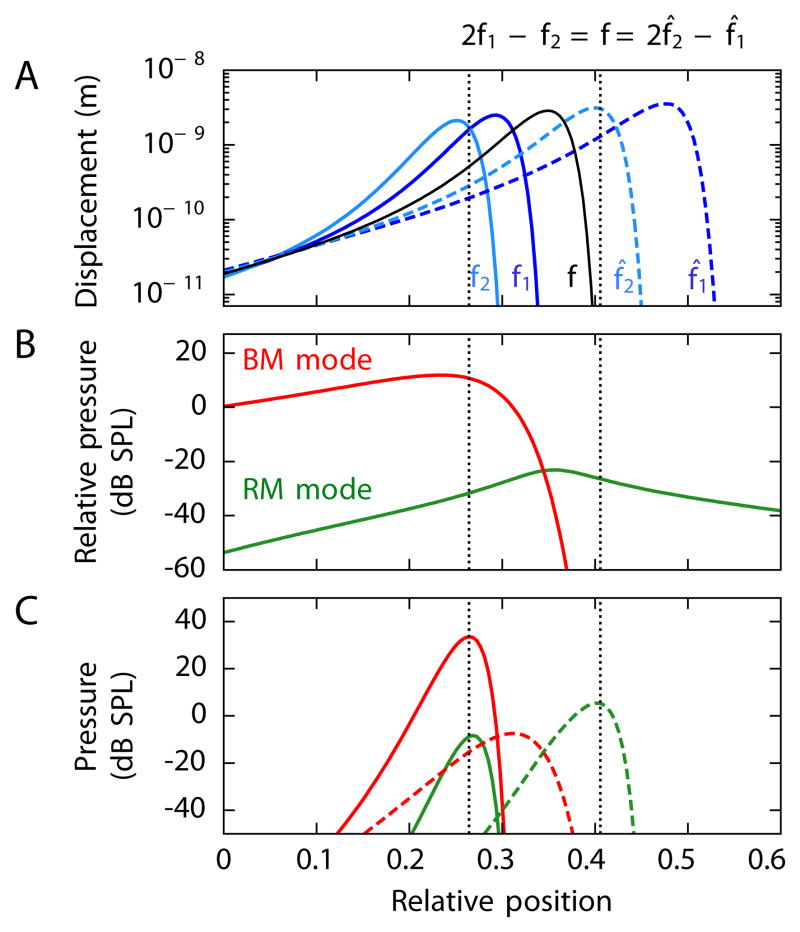
Figure 4. Cochlear origin of distortion-product otoacoustic emissions.
The panels depict the distortion-product otoacoustic emissions computed to emerge from stimulation at 60 dB SPL at frequencies f1 and f2 (solid lines) or f1 and f2 (dashed lines). These frequencies are arranged such that the same distortion product, f = 2000 Hz, emerges either as the lower sideband 2f̂1 − f̂2 or as the upper sideband 2f̂1 − f̂2. The ratios of the primary frequencies in the two instances are f2/f1 =1.3 and f̂2/f̂1 = 1.6. (A) The amplitudes of basilar-membrane waves for each of the stimulus frequencies are shown along with the amplitude of the wave that would emerge for acoustic stimulation at frequency f. The sites of maximal overlap of the waves elicted by stimuli at f1 and f2, as well as the corresponding loci for f̂1 and f̂2, are indicated in this and the two following panels (dotted black lines). (B) Driving the basilar membrane at a frequency f and at varying positions x0 evokes retrograde traveling waves in the Reissner’s membrane mode (green) and basilar-membrane mode (red). The pressures at the stapes are shown relative to the pressure pF at the site of stimulation. The Reissner’s membrane mode can be excited from any cochlear position, whereas the basilar-membrane mode is active only basal to the resonant position. (C) Simultaneous stimulation with sound at frequencies f1 and f2 elicits pressures at the stapes at the distortion frequency f from similar extended cochlear regions (solid lines) for emissions through the two modes. Simultaneous stimulation at f̂1 and f̂2 produces distortion responses (dashed lines) through the two modes that differ in their relative amplitudes and cochlear origins owing to the inability of the distortion products to propagate on the basilar membrane apically to their characteristic places. See Figure S1 and Table S1 for additional details.