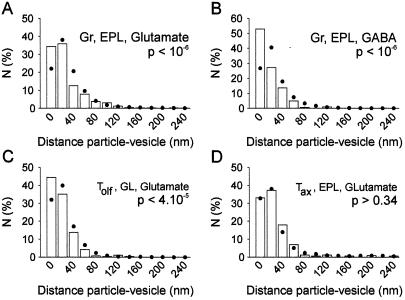
Figure 3.
Quantification of the association of immunoreactivity with synaptic vesicles. Measurements of intercenter distances between each gold particle and the nearest synaptic vesicle were done, and distances were sorted into bins of 20 nm (columns), the y axis showing percent of total in each bin. Distances to the vesicle center from points randomly distributed over the terminal (●) also were calculated (see refs. 40 and 41). (A) Short distances were significantly more represented in experimental distributions compared with random distributions in GC spines labeled for glutamate, indicating that Glu-LI was associated with synaptic vesicles. (B) GABA-LI also was localized to vesicles in GC (Gr) spines. (C) The same was true for Glu-LI in the primary olfactory axon terminals (Tolf) within the glomeruli (GL). (D) By contrast, axon terminals (Tax) from centrifugal neurons making asymmetric contacts with GC dendrites in the EPL (3) contained glutamate not associated with synaptic vesicles (χ2 test). Gr Glutamate: 500 gold particles (24 spines); Gr GABA: 260 gold particles (21 spines); Tolf glutamate: 387 gold particles (13 terminals); Tax: 282 gold particles (11 terminals). Bins not shown amounted to less than 2% of total. χ2 values for comparison of gold particles distribution with random points distribution: Gr (EPL) glutamate, 49.6; Gr (EPL) GABA, 87.6; Tolf GL glutamate, 20.7; Tax EPL glutamate, 2.1.