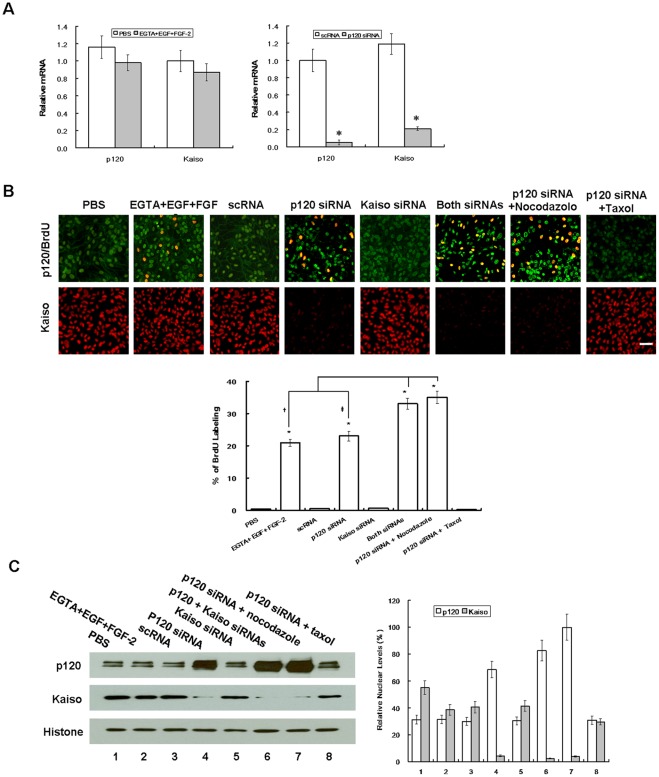
Figure 4. Correlation between BrdU labeling and nuclear translocation of p120 and nuclear release of Kaiso.
ARPE-19 cells cultured to day 7 post-confluence were treated with PBS or 1 mM EGTA with 10 ng/ml EGF plus 20 ng/ml FGF-2 for 1 day, or transfected with 100 nM scRNA or siRNA to p120, Kaiso, or both for 2 days, and cultured in the presence of 10 μm BrdU for 4 h before fixation with acid/methanol. During p120 siRNA transfection, some cultures were added with 5 μg/ml nocodazole or 10 ng/ml taxol. (A) qRT-PCR showed that p120 and Kaiso transcripts remained unchanged by EGTA+EGF+FGF-2 but were 20- and 6-fold suppressed, respectively, by p120 siRNA. (B) As expected, the BrdU labeling index was significantly increased by EGTA+EGF+FGF-2 and p120 siRNA. Compared to scRNA, the BrdU labeling was not changed by Kaiso siRNA alone, but was significatly incrased when Kaiso siRNA was added with p120 siRNA. Compared to p120 siRNA, the BrdU labeling was further promoted from 23% to 35% by nocodazole, but decreased to 0.2% by taxol. Such changes of BrdU labeling index was correlated with increasing p120 nuclear staining and decreasing Kaiso nuclear staining. (C) The above changes were supported by Western blot which showed an inverse relationship between the p120 level and the Kaiso level in nuclear extracts using histone as the loading control. Scale bar indicates 100 μm, while *, †, and ‡ denote P<0.05.