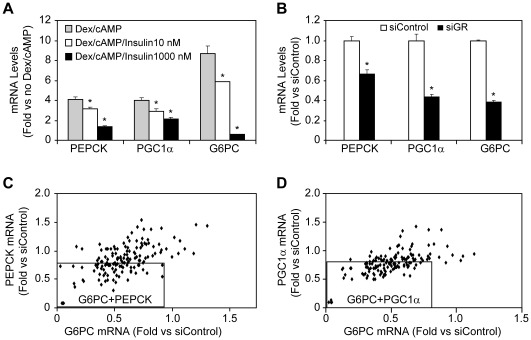
Figure 5. Use of a multiplex HTG assay to identify confirmed hit siRNA pools that decrease expression of key gluconeogenic genes in addition to G6PC.
A. Dex/cAMP increases and insulin dose-dependently reduces AH-G6PC cell PEPCK, PGC1α, and G6PC mRNA expression. Data are presented as the means ± SEM of fold change relative to untreated cells in 3 independent experiments. B. Knockdown of GR by siRNA significantly reduces PEPCK, PGC1α, and G6PC mRNA in AH-G6PC cells incubated with Dex/cAMP and 10 nM insulin. Data are presented as the means ± SEM of fold change relative to mRNA expression in siControl-transfected cells in 3 independent experiments. C. Subsets of pooled siRNAs targeting confirmed hits regulate G6PC and PEPCK, or D. G6PC and PGC1α mRNA expression, in AH-G6PC cells treated with Dex/cAMP and 10 nM insulin. Data in Figures 5C and 5D are plotted as fold change relative to mRNA expression in siControl-transfected cells and are the means of 3 independent experiments. The squares contains siRNAs that reduced both G6PC and PEPCK (C) or G6PC and PGC1α (D) expression by 20% and 15%, respectively.