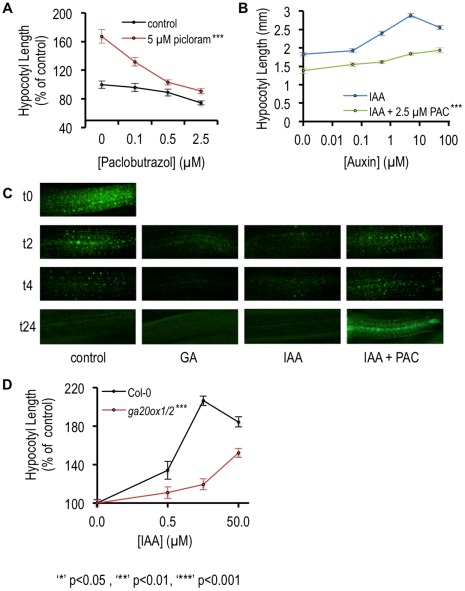
Figure 5. Gibberellin biosynthesis is required for hypocotyl auxin response.
(A,B,C) Asterisk represents mutants showing a significantly different response to hormone treatment compared to wildtype or control treatment. A general linear model (glm performed in R using the car package [101]) was used to determine significance and main effects for genotype were confirmed using ANOVA type III sums of squares. All assumptions for GLM were fulfilled. (A)_Paclobutrazol inhibits hypocotyl auxin response. Hypocotyl length of wild-type seedlings grown in short-day conditions and treated with paclobutrazol at the indicated concentrations (black line) or paclobutrazol plus 5 µM picloram (red line) was measured following 48 hours of treatment. Error bars indicate standard error. (B) Paclobutrazol-mediated inhibition of hypocotyl elongation is not overcome by higher auxin concentration. Hypocotyl length of wild-type seedlings treated with IAA (blue line) or picloram (red line) at the indicated concentrations or IAA and 2.5 µM paclobutrazol (PAC; green line) was measured following 48 hours of treatment. Error bars indicate standard error. (C) RGA protein degrades in response to auxin treatment in hypocotyls of auxin-treated seedlings. Abundance of RGA-GFP protein in hypocotyl tissues was analyzed by epifluorescence microscopy over a 0–24 hour time course. Three day-old seedlings were treated for 2, 4, or 24 hours with 50 µM GA3, 5 µM IAA, 5 µM IAA +2.5 µM paclobutrazol, or a solvent control, prior to imaging. (D) A GA biosynthesis mutant is partially auxin-resistant. Hypocotyl length of wild-type seedlings (Col-0) or the ga20ox1/ox2 mutant [98] treated with IAA at the indicated concentrations was measured following 48 hours of auxin treatment. Hypocotyl length on auxin is shown as a percentage of length on control medium. Error bars indicate standard error.