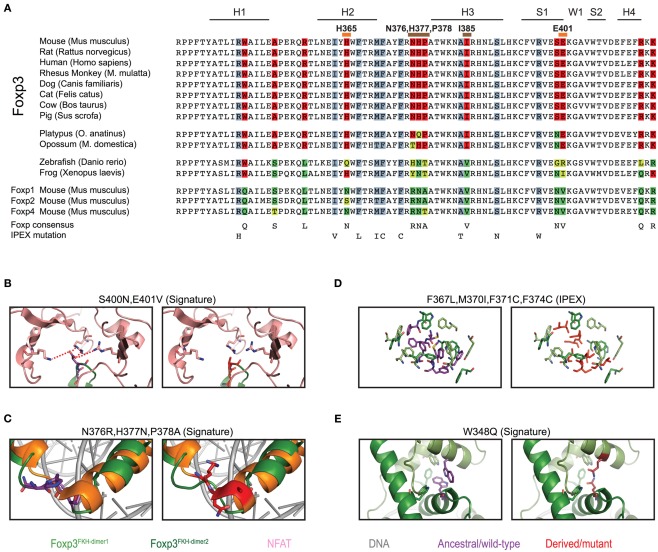
Figure 8.
Mammalian evolution of the forkhead. (A) Alignment of Foxp subfamily FKH domains. Foxp3-specific signature residues are highlighted in red, whereas those of other Foxp subfamilies are highlighted in shades of green. IPEX mutations are underlaid in blue. Signature residues predicted to be involved in NFAT interaction or to affect DNA binding are marked with orange and brown lines respectively (H, helix; S, β-sheet; W, wing). (B–E) Predicted effects of signature residue and IPEX mutations on the structure of Foxp3. Wildtype residues are shown in the left panel, whereas mutants/Foxp consensus residues are shown on the right. Red lines represent attractive forces. (C) Structure alignment of helix 2 and 3 of the FKH of Foxp3 (green; Bandukwala et al., 2011) and Foxp2 (orange; Stroud et al., 2006) with the Foxp3-specific (left panel; purple) and Foxp2 (right panel; red) residues highlighted.