Fig. 7.
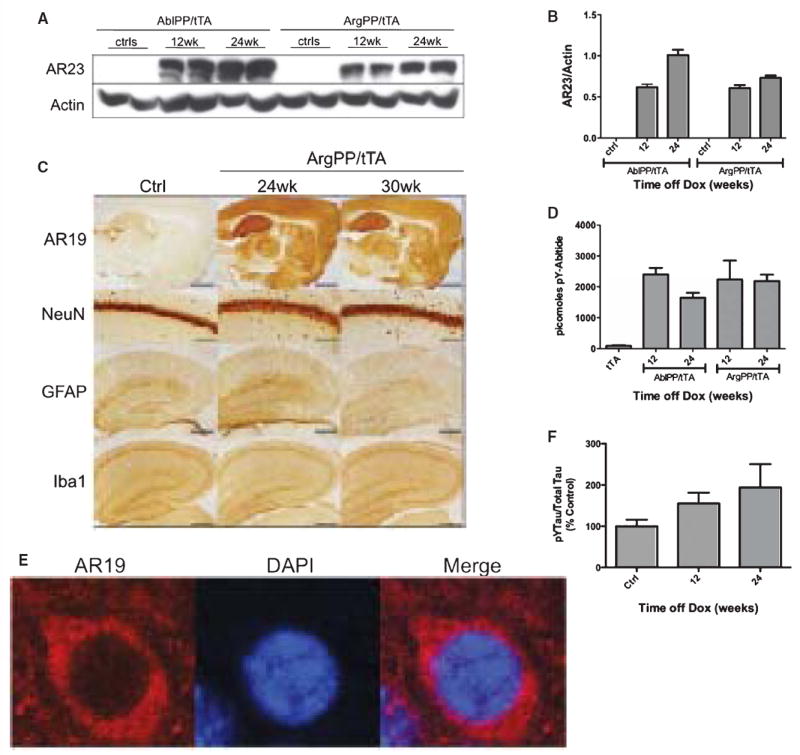
ArgPP/tTA mice do not differ significantly from controls. A) AblPP/tTA and ArgPP/tTA exhibit similar levels of protein expression. Western blotting with AR23 antibody of AblPP/tTA and ArgPP/tTA mouse cortex homogenates 12 and 24 weeks off doxycycline. B) Densitometry analysis of Western blotting in 7A. No significant differences were found between AblPP and ArgPP expression in the two lines of mice. C) Representative sections of control mice and ArgPP/tTA mice 24 and 30 weeks off dox stained for AR19, NeuN, Iba1, and GFAP. Scale bars = 8 mm (AR19), 800 μm (NeuN), 2 mm (GFAP and Iba1). D) Abl activity ELISAs of AblPP/tTA and ArgPP/tTA mouse cortex. Average picomoles of Abltide phosphorylated per kinase reaction, n = 4 per timepoint. E) Arg is expressed in neuronal cell bodies in the ArgPP/tTA mouse. Immunofluorescence of ArgPP/tTA mouse cortex with AR19 (red) and DAPI. F) ELISA analysis of tyrosine phosphorylated (4G10) tau/total (DA9) tau in ArgPP/tTA mice 12 and 24 weeks off dox. n = 4 for each timepoint. One-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s post-test was used to calculate whether ArgPP/tTA mice showed significant increases in tau phosphorlylation when compared to control mice. No significant differences in tau phosphorylation were found.
