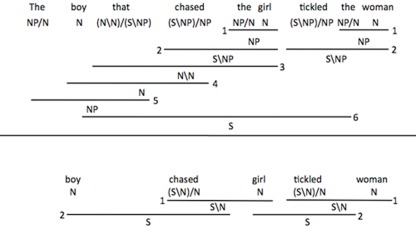
Figure 1.
Syntactic derivations from combinatory categorial grammar (CCG). In this formalism, functions are represented by the schema (X/Y) or (X/Y), in which X is the output of the function, Y is the required argument, and the slash tells whether the argument must be found to the left or to the right of the function. For example, syntactic combination of the (NP/N) and girl (N) yields the girl (NP). (A) Parsing the subject with the subject relative clause requires the integration of material at levels 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5. Comprehension of the entire sentence requires additional integration steps at levels 1, 2, and 6. (B) A shallow heuristic parse of the content words from the subject phrase can be accomplished by integrating material only at levels 1 and 2, yielding the correct thematic role assignment. However, use of the same strategy on the second NVN sequence yields the wrong agent for the verb tickled.