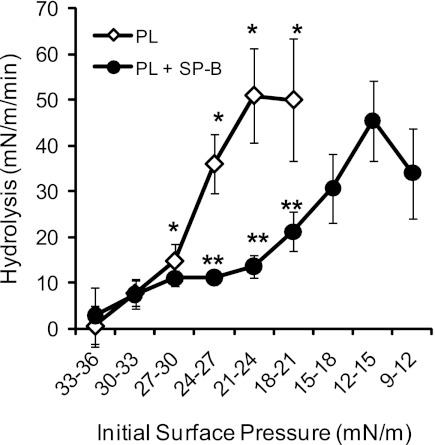
Fig. 6.
SP-B inhibition of monomolecular film hydrolysis is surface pressure dependent. Hydrolysis of monomolecular film PL by Group IB sPLA2 was performed as outlined in Fig. 5 in the presence and absence of SP-B (5%). Enough PL was added onto the film to achieve the desired initial surface pressure (10–50 mN/m). Hydrolysis was measured as the rate of change in surface pressures (mN/m per min) across the specified range of initial surface pressure (mN/m). No PL hydrolysis, seen as a significant rate of change in surface pressure, was seen after addition of sPLA2 at initial surface pressures >30 mN/m. At pressures below 30 mN/m, SP-B inhibited the sPLA2-mediated hydrolysis of surfactant PL, in part by shifting required hydrolysis to lower surface pressures. *P < 0.05 for PL rates vs. those at 30–33 mN/m initial pressure, **P < 0.05 for SP-B inhibition of sPLA2 hydrolysis of PL at same initial pressures.