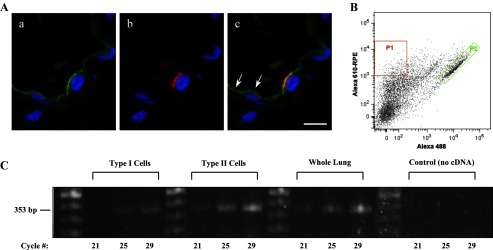
Fig. 6.
CEACAM6 expression in adult alveolar epithelial cells. A: representative high-magnification images of immunostaining from cryosections of inflation-fixed peripheral lung (alveolar region). a: CEACAM6 signal (green) of differing intensity is observed in cells of the alveolar epithelium. b: HTII-280 (red) signal in the same field as a, showing one positive type II cell in the field. c: Merge of a and b, with yellow signal showing colocalization of CEACAM6 and HTII-280; CEACAM6 signal also occurs in type I cells on either side of the type II cell (e.g., arrows). Blue, DAPI in all images; n = 2 lungs; bar = 10 μm. B: scattergram of human alveolar type I and type II cells isolated by FACS. Two cell populations were selected: P1 (red), high anti-HTI-56 Alexa 610-RPE-staining type I cells; and P2 (green), high anti-HTII-280 Alexa 488-staining type II cells. C: agarose gel electrophoresis after RT-PCR for CEACAM6 of type I cells and type II cells, isolated by FACS sorting, as well as whole lung tissue from the same lung. CEACAM6-specific primers identified product at the expected size of 353 bp from each RNA preparation, whereas no product was observed in the no cDNA control; cycle numbers = 21, 25, and 29.