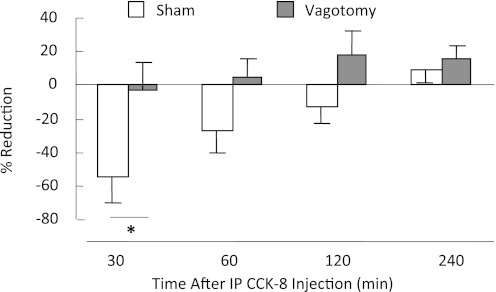
Fig. 1.
Percent reduction of intake of powdered rodent diet following intraperitoneal injection of CCK-8 (2 μg/kg) in vagotomized and sham-vagotomized rats. Compared with intraperitoneal saline injection, intraperitoneal CCK-8 injection significantly reduced food intake in 16-h, food-deprived, sham-operated control rats (sham, n = 8), but it did not reduce food intake in vagotomized rats (n = 5). Following saline injection, sham-operated control rats ate 5.3 ± 0.3 g in 30 min, which was significantly reduced to 2.4 ± 0.8 g following intraperitoneal CCK-8 (P < 0.005). By contrast, vagotomized rats ate 4.5 ± 0.6 g after saline injection, which was not significantly different from their intake after intraperitoneal CCK-8 (4.3 ± 1.0g; P > 0.5). *Significant difference (P < 0.01) in CCK-induced reduction of intake between vagotomized and sham-vagotomized rats.