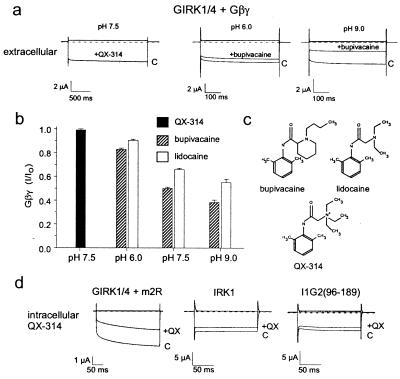
Figure 3.
Effect of neutral and charged forms of local anesthetics on GIRK channels. (a) Oocytes were injected with the cRNA for GIRK1 and GIRK4 subunits plus Gβ1γ2 subunits. Current responses elicited by voltage steps to +50 and −100 mV are shown for extracellular QX-314 (500 μM) and bupivacaine (100 μM) at pH 6.0 and 9.0. The K+ current changed less than 10% when switching among different pH solutions. (b) Fractional current remaining (Gβγ, I/Io) is shown for 100 μM QX-314 (pH 7.5, n = 5), 100 μM bupivacaine (pH = 6, 7.5, and 9; n = 6), and 100 μM lidocaine (pH = 6, 7.5, and 9; n = 6). (c) Chemical structures for bupivacaine, lidocaine, and QX-314. (d) Intracellular QX-314 inhibits G protein activation of GIRK channels but not I1G2(96–189). Oocytes were injected with the cRNA for GIRK1, GIRK4, and m2 muscarinic receptor, IRK1, or chimera I1G2(96–189). Current responses were elicited by voltage steps from +50 and −100 mV (VH = 0 mV) before and then 30–60 min following the injection of QX-314 into the same oocyte (n = 6). The carbachol-induced (+carb-basal) current is shown for GIRK1/4.