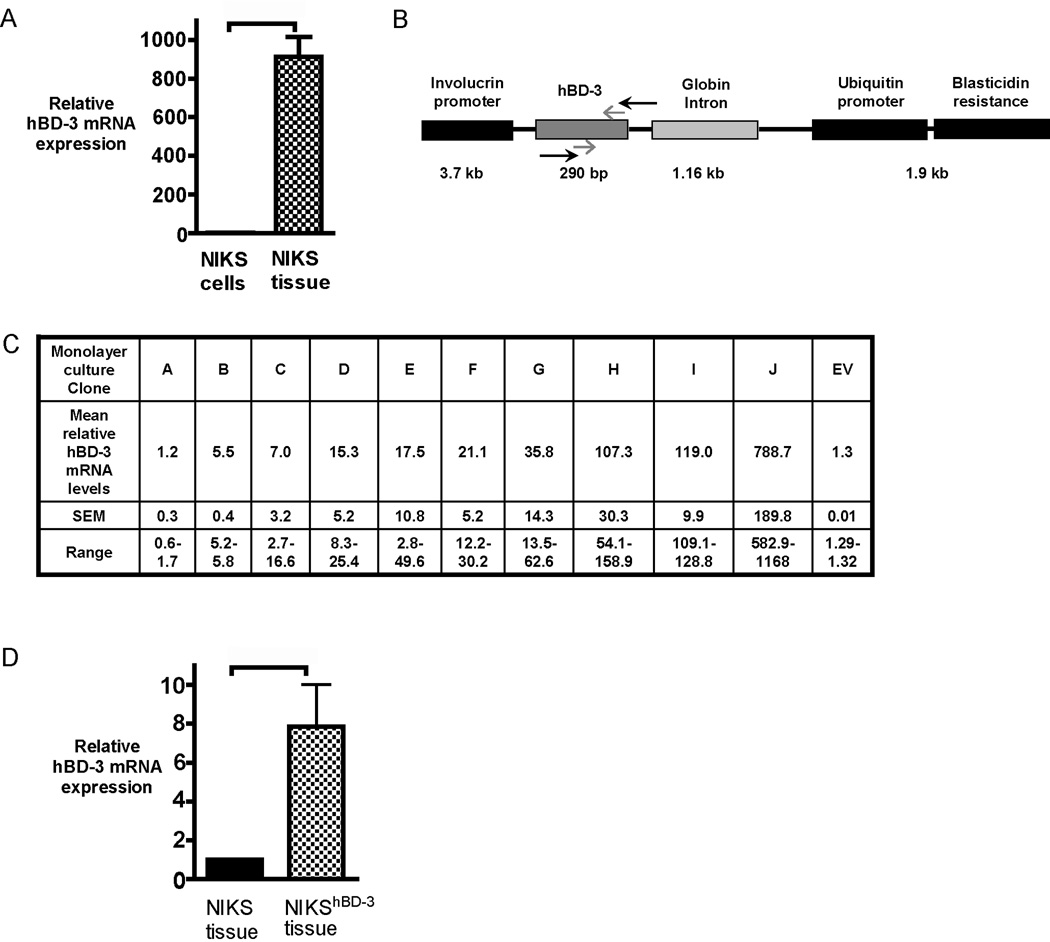
Figure 1. Generation of a stable NIKS keratinocyte cell line exogenously expressing hBD-3.
(A) hBD-3 mRNA expression measured by qPCR of skin substitute tissue generated with NIKS keratinocytes (NIKS tissue) compared with post-confluent monolayer cultures of NIKS keratinocytes (NIKS cells). hBD-3 mRNA expression in NIKS tissue is expressed as a fold change relative to expression in NIKS monolayer arbitrarily set at 1. Bars represent mean + SEM (n=3). p value = 0.0031 calculated with the Wilcoxon signed rank test. (B) Schematic representation of the construct used for genetic engineering of NIKS keratinocytes. Black arrows represent primers used in RT-PCR to detect transgene expression for the initial clone screen to identify clones containing the construct. Grey arrows show approximate positions of qPCR amplified endogenous and transgene hBD-3. Sizes of gene products listed are not to scale. (C) Total hBD-3 mRNA expression (endogenous and exogenous) of NIKShBD-3 clones, designated A–J, in post-confluent monolayer cultures. Values are expressed as a fold change relative to hBD-3 mRNA expression in unmodified NIKS arbitrarily set at 1. Fold change is represented as the mean and standard error of the mean (SEM) of experimental. Empty Vector clone containing Inv-Ub-bsd construct without the hBD-3 insert is designated as EV. (D) hBD-3 mRNA expression measured by qPCR of NIKS tissue and NIKShBD-3 (Clone J) tissue. Values are expressed as a fold change relative to hBD-3 mRNA expression in untransfected NIKS tissue arbitrarily set at 1. Bars represent mean + SEM (n=3). p=0.0206 calculated with the Wilcoxon signed rank test, using logarithmic transformation of fold change for quantitative PCR data.