Fig. 1.
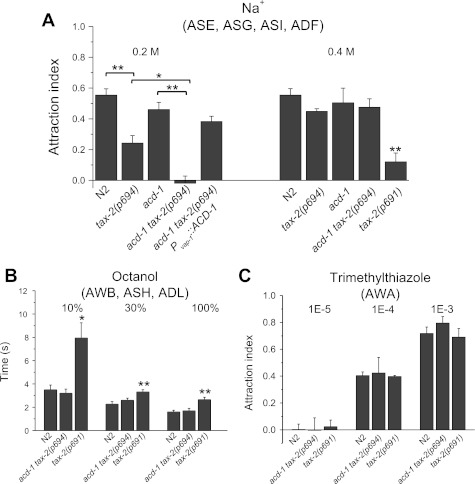
Knockout of glial channel acd-1 worsens reduced attraction to Na+ of tax-2(p694) mutants. A: chemotaxis to 0.2 and 0.4 M Na+ was determined for wild-type Caenorhabiditis elegans (N2) and for acd-1, tax-2(p694), acd-1 tax-2(p694), acd-1 tax-2(p694); Pvap-1::ACD-1, and tax-2(p691) mutants. Number of assays was 15, 11, 7, 7, and 12 for 0.2 M Na+ and 14, 7, 8, 7, and 4 for 0.4 M Na+, respectively, with 30 animals used in each assay. tax-2(p694) mutant animals were less attracted to 0.2 M Na+ than other animals, and knockout of acd-1 worsened this chemotaxis defect. The chemotaxis index for acd-1 knockout animals is not statistically different from that of wild type. Data are means ± SE. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01 (ANOVA). Chemotaxis to Na+ is mediated primarily by ASE neurons and to a lesser extent by ASG, ASI, and ADF neurons (Bargmann and Horvitz 1991). B: repulsion by octanol was normal in acd-1 tax-2(p694) double mutants but defective in tax-2(p691) mutants. The time that animals took to respond to octanol at 3 dilutions was recorded. Number of animals tested was 10, 10, and 16 for 10% octanol; 38, 20, and 25 for 30% octanol, and 25, 20, and 26 for 100% octanol. Data are means ± SE. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01 (ANOVA). Octanol is sensed by AWB, ASH, and ADL neurons (Troemel et al. 1997). C: attraction to trimethylthiazole mediated by AWA neurons was normal in tax-2(p691) and acd-1 tax-2(p694) mutant animals. Attraction to trimethylthiazole at 3 dilutions was assayed. Wild type and mutants did not respond to the most diluted concentration. Number of assays was 4, 3, and 3 for 1E-5 dilution; 6, 3, and 3 for 1E-4 dilution; and 3, 4, and 3 for 1E-3 dilution with 30 animals used in each assay. Data are means ± SE.