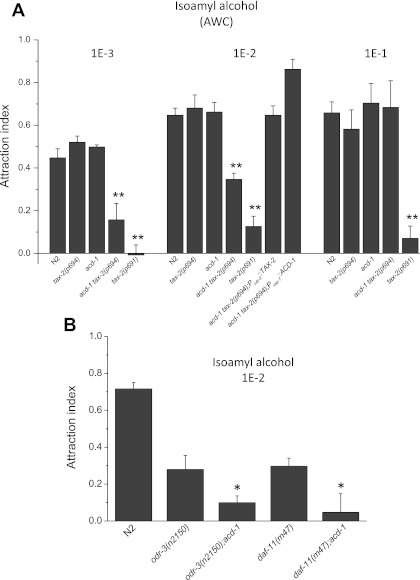
Fig. 2.
Knockout of acd-1 unmasks a chemotaxis defect in tax-2(p694) mutants and worsens sensory deficits caused by mutations in signaling genes odr-3 and daf-11. A: chemotaxis to isoamyl alcohol at 1E-3, 1E-2, and 1E-1 dilutions was determined for wild-type C. elegans (N2) and for acd-1, tax-2(p694), acd-1 tax-2(p694), and tax-2(p691) mutants. At 1E-2 dilution, chemotaxis of acd-1 tax-2(p694); Podr-3::TAX-2 and acd-1 tax-2(p694); Pvap-1::ACD-1 animals was also determined. Number of assays was 9, 4, 4, 13, and 4 for 1E-3 dilution; 14, 8, 19, 17, 6, 7, and 7 for 1E-2 dilution; and 4, 6, 3, 3, and 3 for 1E-1 dilution with 30 animals used in each assay. AWC neurons mediated attraction to isoamyl alcohol. **P < 0.01 compared with wild type (ANOVA). Data are means ± SE. B: attraction to isoamyl alcohol at 1E-2 dilution was assayed as described in A. Number of assays for wild type (N2), odr-3(n2150), acd-1;odr-3(n2150), daf-11(m47), and acd-1;daf-11(m47) animals was 12, 13, 13, 10, and 11, respectively, with 30 animals used in each assay. Data are means ± SE. *P < 0.05 compared with odr-3 and daf-11 single mutants (ANOVA).