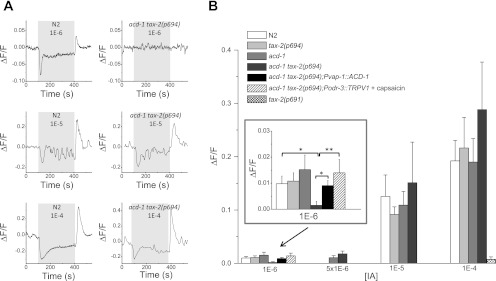
Fig. 4.
Reduced Ca2+ responses on exposure to isoamyl alcohol in AWC neurons of acd-1 tax-2(p694) double-mutant animals. A: examples of Ca2+ responses elicited by perfusion with isoamyl alcohol at 1E-6, 1E-5, and 1E-4 dilutions in AWCon neurons of wild-type (N2) and acd-1 tax-2(p694) double-mutant animals as indicated. Ca2+ decreases on perfusion with the odor and increased on odor removal (Chalasani et al. 2007). Ca2+ changes were detected in only 1 AWCon neuron of acd-1 tax-2(p694) double-mutant animals at 1E-6 out of 22 examined. Gray box indicates the time of perfusion with isoamyl alcohol. Ca2+ changes are reported as changes in GCaMP1.0 fluorescence (ΔF/F) expressed in AWCon neurons (Chalasani et al. 2007). B: average increase of fluorescence, and thus Ca2+, on odor removal in wild-type (N2), tax-2(p694), acd-1, and acd-1 tax-2(p694) mutant animals at different concentrations as indicated. At 1E-4 dilution, Ca2+ changes in AWCon neurons of tax-2(p691) mutants are also shown. Inset represents a larger scale for the data at 1E-6 dilution. At this concentration, Ca2+ changes on odor removal in acd-1 tax-2(p694); Pvap-1::ACD-1 and acd-1 tax-2(p694); Podr-3::TRPV1 animals in the presence of capsaicin (50 μM) are also shown. Number of animals analyzed was 20, 14, 17, 22,10, and 10 for 1E-6 dilution; 15 and 9 for 5E-6 dilution; 7, 11, 6, and 5 for 1E-5 dilution; and 23, 8, 7, 9, and 12 for 1E-4 dilution. Data are means ± SE. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01 (ANOVA). [IA], isoamyl alcohol concentration.