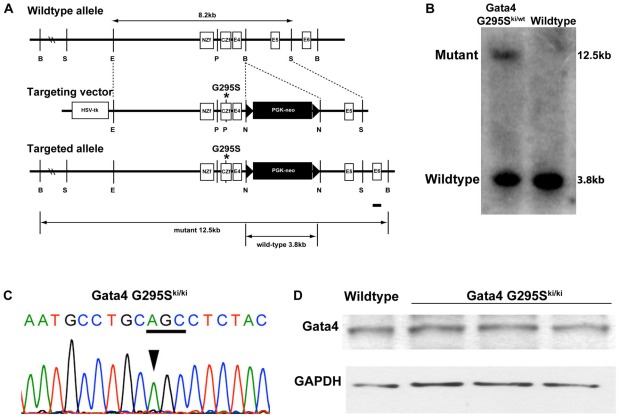
Figure 1. Targeting strategy for generation of Gata4 G295S knock-in mice.
(A) Single nucleotide change resulting in the glycine to serine mutation was introduced into the mouse Gata4 locus. Partial restriction map of the murine Gata4 wildtype allele (top), the Gata4 targeting vector (middle), and successfully targeted allele (bottom) are shown. Homologous recombination results in replacement of wildtype Gata4 with genomic DNA harboring a substitution of glycine to serine at position 295 into the mouse Gata4 locus, as well as the incorporation of neomycin cassette surrounded by loxP sites. Gata4 coding exons are shown as empty boxes, whereas the exon used as a probe used for Southern blot analysis is highlighted by a black bar. NZf, amino- terminal zinc finger (exon 2); CZf, carboxy- terminal zinc finger (exon 3); E4, exon 4; E5, exon 5; E6, exon 6; B, BglI; S, SacI; E, EcoRV; and N, NotI. (B) Germline transmission of mutant allele was confirmed by Southern blotting after digestion of genomic DNA from Gata4 G295Ski/wt and wiltype mice with BglI. A 3.8 kb wildtype band and a 12.5 kb mutant band using 3′ external probe are shown (black bar in A). (C) Direct sequencing confirmed the presence of mutated residue that altered glycine (GGC) to serine (AGC) in DNA from Gata4 G295Ski/ki embryos. (D) Western blotting demonstrates that levels of Gata4 protein are equivalent in Gata4 G295Ski/ki hearts (from three different embryos) as compared to wildtype E9.5 hearts. Equal protein loading is shown by Western blotting to GAPDH.