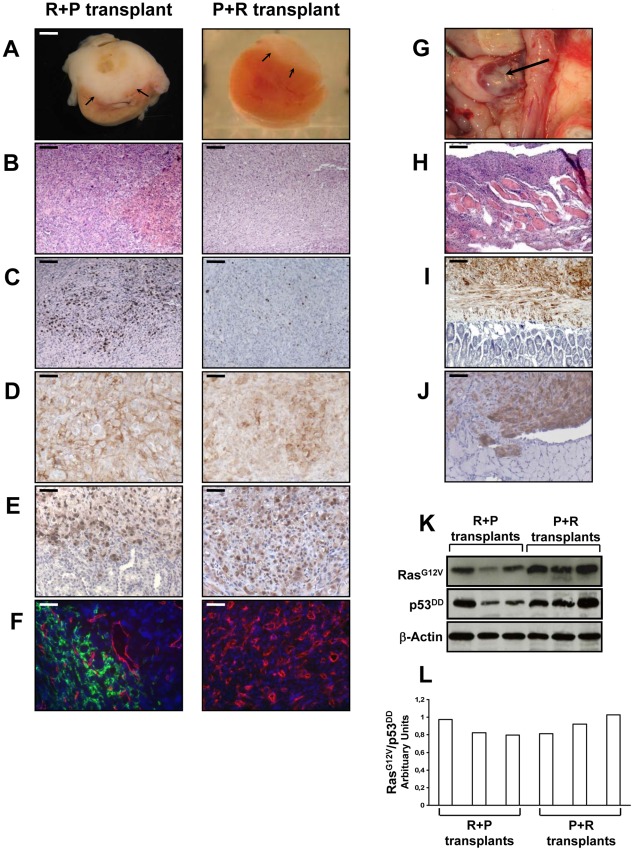
Figure 5. In vivo characterization of tissues formed at day 35 following the transplantation of R+P or P+R cells.
A–F, 2×106 R+P or P+R cells were transplanted under the kidney capsule of Scid mice. Xenografted tissue masses were removed from the animals at day 35 after cell transplantation and cut transversally showing internal tissue above the kidney (arrows) (A). Paraffin-embedded tissues were sectioned and H&E stained (bar, 100 µm) (B); assayed for Ki-67+ cells (bar, 100 µm) (C); immunostained for Ras (bar, 50 µm) (D); immunostained for p53 (bar, 50 µm) (E); and double CD31 (red) and LYVE-1 (green) immunofluorescence stained (no green fluorescence detected for the P+R transplant) (bar, 50 µm) (F). G–J, macroscopic intraperitoneal tumor spread on the spleen of mice after implantation of adrenocortical R+P cells (arrow) (G); and microscopic tumor spread in the abdominal muscle (H&E staining, bar, 400 µm) (H); in the intestines, immunostained for Ras (bar, 100 µm) (I); and in the diaphragm, immunostained for p53 (bar, 100 µm) (J); Western blot analysis of introduced genes. Expression of RasG12V and p53DD was confirmed in three separate R+P and P+R tranplants. Actin served as a loading control (K). Ratio of RasG12V to p53DD of R+P and P+R transplants (L).