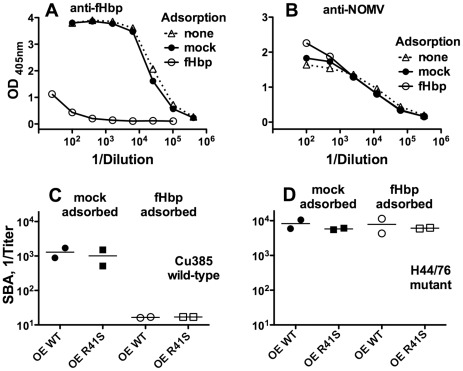
Figure 4. Effect of depletion of serum anti-fHbp antibodies on bactericidal activity.
A, IgG anti-fHbp antibody as measured by ELISA. Representative data are from one of the two serum pools from wild-type mice immunized with the NOMV with over-expressed WT fHbp. The serum pool either was not adsorbed (“none,” open triangles with dotted line), or adsorbed on a human albumin column (“mock,” filled circles with solid line), or on an fHbp column (“fHbp,” open circles with solid line). The adsorbed serum samples were adjusted to the original volume applied to the column. B, IgG anti-NOMV antibody measured by ELISA with the NOMV vaccine prepared from fHbp knock-out strain as the antigen in the wells. Data are from the same serum pool as shown in Panel A. For panels A and B, similar respective data were obtained with each of the other three serum pools. C, Serum bactericidal antibody responses against strain Cu385, which has a fHbp variant group 1 antigen matched to that of the vaccines and a mismatched PorA (see Table 1). Two serum pools for each vaccine group were assayed (NOMV with over-expressed WT fHbp (“OE WT”) or R41S mutant fHbp (“OE R41S”) following depletion on mock or fHbp columns. D. Serum bactericidal antibody titers measured against an isogenic mutant of strain H44/76 with matched PorA to that of the vaccine strains and a mismatched fHbp in variant group 3. The respective serum pools were the same as in Panel C.