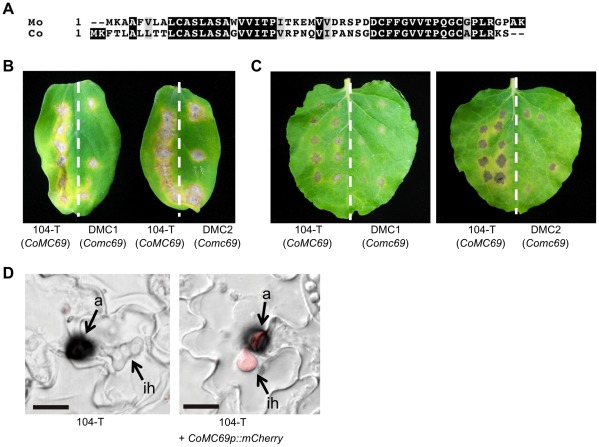
Figure 8. CoMC69 is involved in fungal pathogenicity of C. orbiculare.
(A) Sequence alignment of MC69 between M. oryzae (Mo) and C. orbiculare (Co). Amino acid sequences were aligned using Clustal W program [52]. Identical amino acids are indicated as white letters on a black background. Similar residues are shown by gray background. Gaps introduced for alignment are indicated by hyphens. (B) Pathogenicity test of the Comc69 mutants on cucumber. Conidial suspensions were inoculated on detached cotyledons of cucumber (Cucumis sativa). On the left half of the cotyledons, the wild-type strain 104-T was inoculated as positive control. On the right half, the Comc69 strains (DMC1 and DMC2) were inoculated. Inoculated cotyledons were incubated for 7 days. (C) Pathogenicity test of the Comc69 mutants on N. benthamiana. On the left half of the detached leaves of N. benthamiana, the strain 104-T was inoculated as positive control. On the right half, the Comc69 strains (DMC1 and DMC2) were inoculated. Inoculated leaves were incubated for 7 days. (D) mCherry-based reporter assay for expression of the CoMC69 gene. Conidia from the C. orbiculare strain carrying the CoMC69 promoter-mCherry fusion gene (CoMC69p::mCherry) was inoculated onto the lower surfaces of cucumber cotyledons, and the inoculated plant was incubated for 4 days. a, appressorium; ih, intracellular hypha. Scale bars = 10 µm.