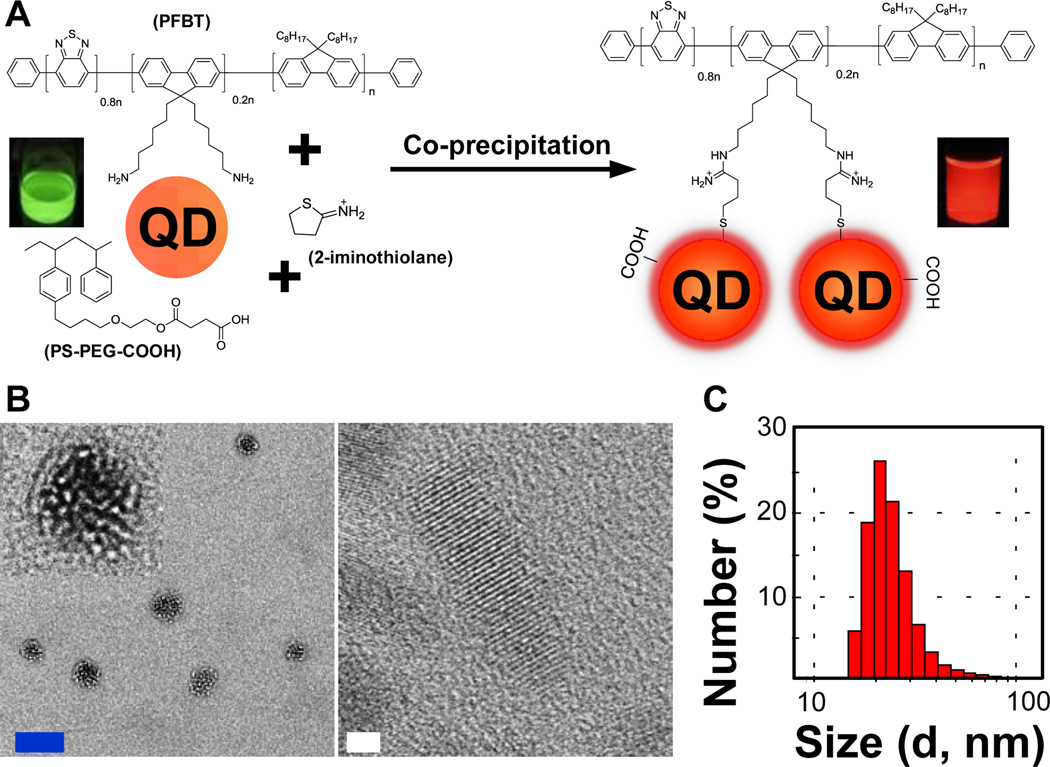
Figure 1.
(A) Schematic showing the preparation of Pdot-Qdot hydrid nanoparticles (NPs). PFBT with amino terminal groups was converted to thiols first in order to covalently bind PFBT to the surfaces of Qdots, after which the Pdot-Qdot solution was mixed with PS-PEG-COOH in THF and then co-condensed in water via nanoprecipitation under vigorous sonication to form Qdot-embedded Pdots. (B) TEM (transmission electron microscopy) images of Pdot-Qdot NPs. The inset in the upper-left corner shows the enlarged view of a single Pdot-Qdot NP. The blue and white scale bars represent 20 nm and 2 nm, respectively. (C) DLS (dynamic light scattering) measurements showing the hydrodynamic diameters (histogram; average diameter was ~25 nm) of Pdot-Qdot NPs. QD represents Qdot.