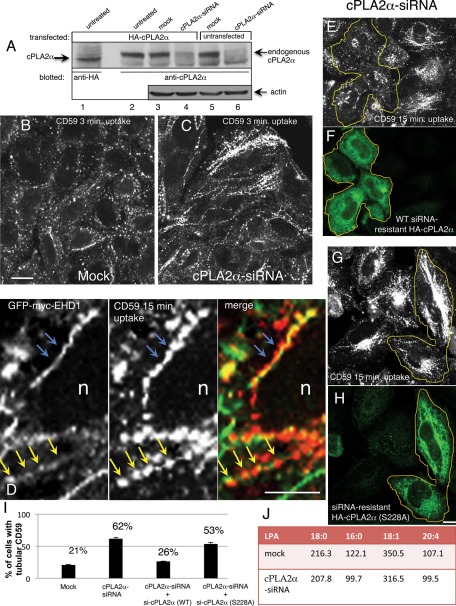
FIGURE 1:
Depletion of cPLA2α induces hypertubulation of CD59-containing endosomes. (A) Untransfected (lanes 5 and 6) or HA-cPLA2α–overexpressing HeLa cells (lanes 1–4) were mock treated (lanes 3 and 5) or treated with cPLA2α-siRNA for 2 d (lanes 4 and 6), harvested, and lysed. Lysates were separated by 8% SDS–PAGE, transferred to nitrocellulose filters, and immunoblotted with either mouse anti-HA antibody (lane 1, to identify the band corresponding to the particular α isoform of cPLA2) and anti-cPLA2α antibody (lanes 2–6, to detect endogenous and overexpressed cPLA2α). Actin was probed as a protein loading control (lanes 3–6). Note that a band corresponding to both overexpressed and endogenous cPLA2α is greatly reduced by the siRNA treatment (lanes 4 and 6). (B, C) HeLa cells growing on coverslips were mock treated (B) or treated with cPLA2α–siRNA (C). After 48 h, cells were incubated with mouse anti-CD59 antibody for 3 min at 37°C, acid stripped, and fixed. Internalized CD59 was detected with Alexa 568–conjugated anti-mouse antibody. (D) High magnification of tubular interconnected “beads-on-a-string” endosome. HeLa cells transfected with GFP-myc-EHD1 were allowed to internalize anti-CD59 for 15 min at 37°C, then acid stripped, fixed, and stained with Alexa 568 goat anti-mouse secondary antibody. Blue arrows depict continuous CD59 and EHD1 tubules, and yellow arrows point to the postfixation commonly seen CD59 “beads” within the continuous EHD1-decorated tubular membrane. (E–H) Either siRNA-resistant wild-type HA-cPLA2α (E, F) or active-site mutant (S228A) (G, H) was transfected into cPLA2α-siRNA–treated cells. After 48 h, cells were pulsed with anti-CD59 antibody for 15 min, acid stripped, and fixed. Cells were then stained with rabbit anti-HA antibody to identify cPLA2α-expressing cells, denoted with yellow lines, followed by Alexa 568–conjugated anti-mouse and Alexa 488–conjugated anti-rabbit antibody. (I) Quantification of the percentage of cells with tubular CD59 for mock-treated, cPLA2α-siRNA–treated, and rescue-treated cells by transfecting cells with either siRNA-resistant wild-type HA-cPLA2α or S228A mutant. This experiment was repeated three times, and SE is shown. (J) Cells were either mock treated or treated with cPLA2α-siRNA for 48 h and then scraped and spun down. A small sample of each cell pellet was sonicated and subjected to total protein measurement, whereas the rest of the cell pellet was extracted with acidified 1-butanol (see Materials and Methods). Saturated (18:0, 16:0) and unsaturated (18:1, 20:4) LPA species were analyzed by liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. Data presented represents the average of two independent experiments, and the concentration of each LPA species is given in ng LPA/mg protein. Bar, 10 μm.