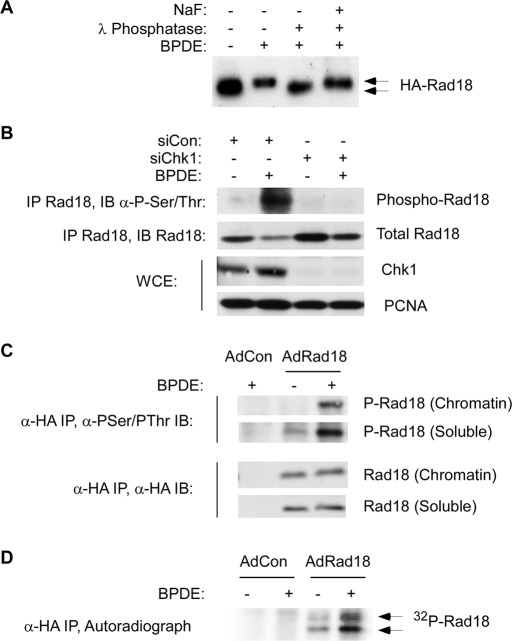
FIGURE 1:
Rad18 phosphorylation is genotoxin inducible and requires Chk1. (A) HA-Rad18–expressing H1299 cells were treated with 600 nM BPDE for 4 h or were left untreated for controls. CSK extracts from the cells were incubated with λ phosphatase (1 U/μl) in the presence or absence of 50 mM NaF at 37 C for 30 min. The resulting extracts were analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-HA antibodies. BPDE-induced electrophoretic mobility shifts are indicated by the arrows. (B) Control or Chk1-depleted HA-Rad18–expressing H1299 cells were treated with 600 nM BPDE for 4 h or were left untreated for controls. Anti-HA immune complexes were analyzed by SDS–PAGE and immunoblotting sequentially with anti–phosphoserine/phosphothreonine and anti-HA antibodies. Whole-cell extracts were analyzed for Chk1 expression, and PCNA was used as a loading control. (C) AdCon or AdHA-Rad18–infected H1299 cells were treated with 600 nM BPDE for 4 h or were left untreated for controls. Chromatin and soluble fractions from the cells were immunoprecipitated with anti-HA antibodies, and the resulting immunoprecipitates were analyzed by SDS–PAGE and immunoblotting with anti–phosphoserine/phosphothreonine and anti-HA antibodies. (D) AdCon or AdHA-Rad18–infected H1299 cells were transferred to phosphate-free DMEM and incubated for 4 h in the presence of 0.2 mCi/ml of 32P-orthophosphate. The 32P-orthophosphate–labeled cells were treated with 600 nM BPDE for 4 h or were left untreated for controls. Whole-cell extracts from the cells were immunoprecipitated with anti-HA antibodies, and the resulting immunoprecipitates were resolved by SDS–PAGE. The resulting gels were washed extensively in 40% methanol/10% acetic acid. The fixed gel was dried, and radioactive proteins were detected by autoradiography.