Fig. 1.
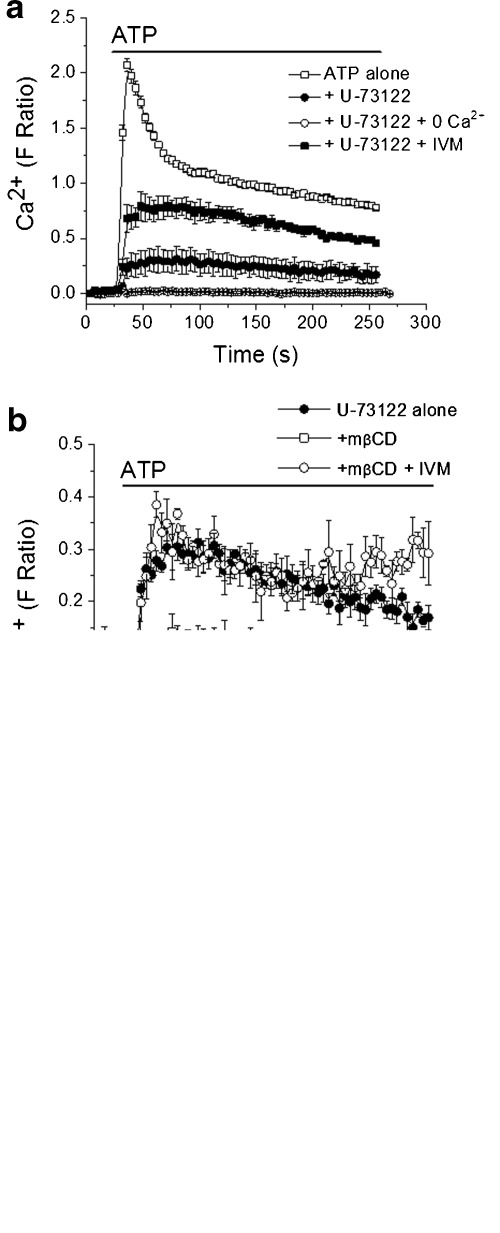
Cholesterol depletion suppresses P2X4-dependent calcium entry in human monocytes. a Pharmacological isolation of P2X4-dependent calcium entry in THP-1 cells. Elevation in [Ca2+]i in response to 100 μM ATP is significantly inhibited by U-73122 though a resistant component remains. (N = 6). The resistant P2X4 component is abolished in the absence of extracellular calcium (0 Ca2+) and potentiated by ivermectin (IVM). b Treatment with the cholesterol depleting agent mβCD (10 mM, 1 h) reduces P2X4-dependent calcium entry (N = 6). c Mean peak calcium response data for 100 μM ATP summarising effect of cholesterol depletion of P2Y and P2X4-dependent calcium entry. (N = 4–6; ***p < 0.01 vs ATP with U-71322; #p < 0.01 vs ATP with U-71322 and mβCD) Note that the U-71322-resistant component is not sensitive to AZ11645373 (1 μM, 30 min), a selective P2X7 antagonist