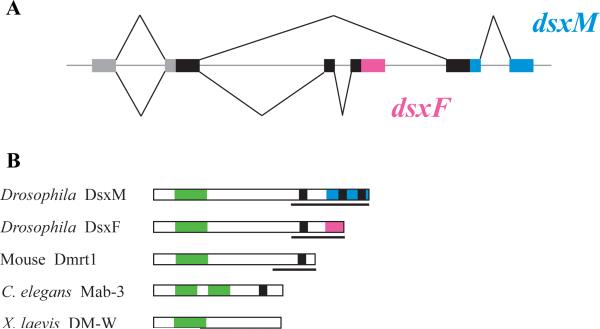
Box 2 Figure I.
The structure of Dmrt genes and proteins. A. Genomic structure of the Drosophila dsx. Coding sequences common to dsxM and dsxF are shown by thick black bars, transcribed untranslated regions by grey bars, and introns and intergenic regions by a thin grey line; splicing patterns are indicated by thin black lines above and below the gene region. dsxM and dsxF share the 5’ exon that encodes the DNA-binding DM domain, but include mutually exclusive 3’ exons that encode different dimerization/activation domains. dsxM-specific exons are shown in blue and dsxF-specific sequence in pink. B. Protein structure of the Drosophila Dsx, mouse DMRT1, C. elegans MAB-3, and Xenopus DM-W. DM domains are shown in green and proline/serine-rich domains found in most DMRT proteins are in black. Pink and blue bars show the sex-specific domains of DsxF and DsxM, respectively. Lines under the protein schematics indicate characterized protein domains involved in transcriptional regulation. MAB-3 is unique in having two DM domains, and DM-W is unusual in lacking a C-terminal regulatory domain.