Figure 1.
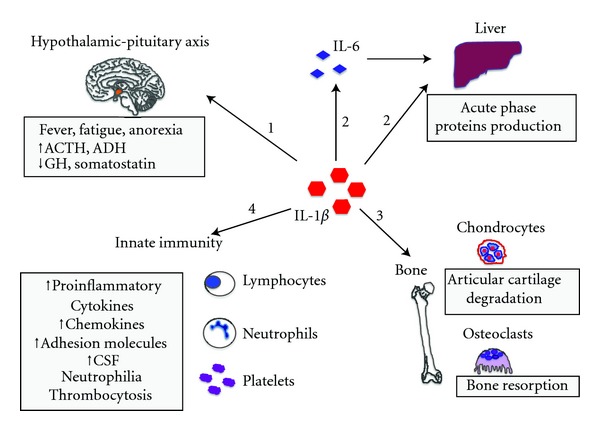
Main effects of IL-1. (1) The action on the hypothalamic-pituitary axis influences the production of the following hormones: adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), growth hormone (GH), vasopressin or antidiuretic hormone (ADH), and somatostatin. IL-1 is responsible for the constitutional symptoms in IL-1-dependent diseases (fever, fatigue, anorexia, and growth delay). (2) Liver synthesis and secretion of acute phase proteins (both by direct IL-1 action and via IL-6 induction). (3) Osteoclasts activation and matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) synthesis by chondrocytes, resulting in bone resorption and cartilage degradation, respectively. (4) Innate immune system cells activation and proliferation, enhanced gene transcription of proinflammatory molecules (inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), cyclo-oxygenase 2 (COX2), and phospholipase A2), proinflammatory cytokines, adhesion molecules, and colony-stimulating factors (CSF).
