Fig. 1.
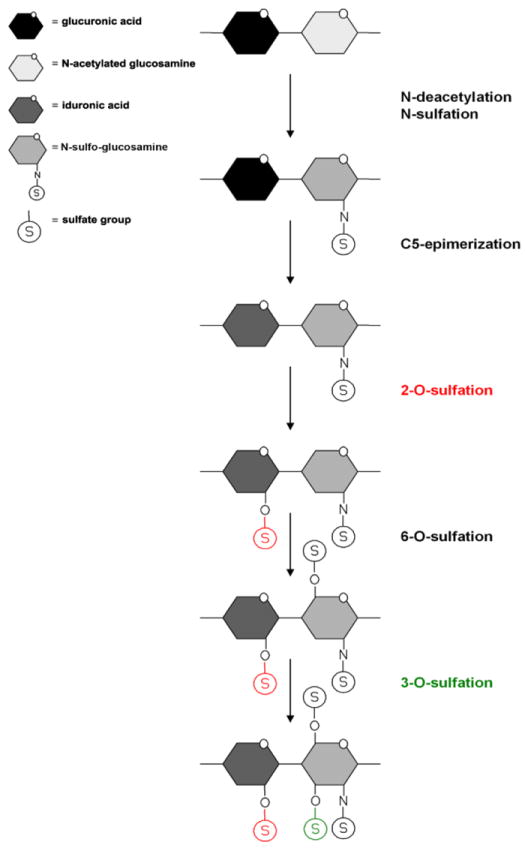
Heparan sulfate modifications. Heparan sulfate chains are initially synthesized as repeating disaccharide units of N-acetylated glucosamine and glucuronic acid. HS can then be modified by a series of enzymatic reactions, including N-deacetylation and N-sulfation of N-acetylated glucosamine converting it to N-sulfo-glucosamine, C5 epimerization of glucuronic acid to iduronic acid, and O-sulfation at the 2-OH, 6-OH, and 3-OH positions. First is 2-O-sulfation of iduronic acid and glucuronic acid, followed by 6-O-sulfation of N-acetylated glucosamine and N-sulfo-glucosamine units, and finally 3-O-sulfation of glucosamine residues. 2-O (red) and 3-O (green) sulfations are highlighted.
