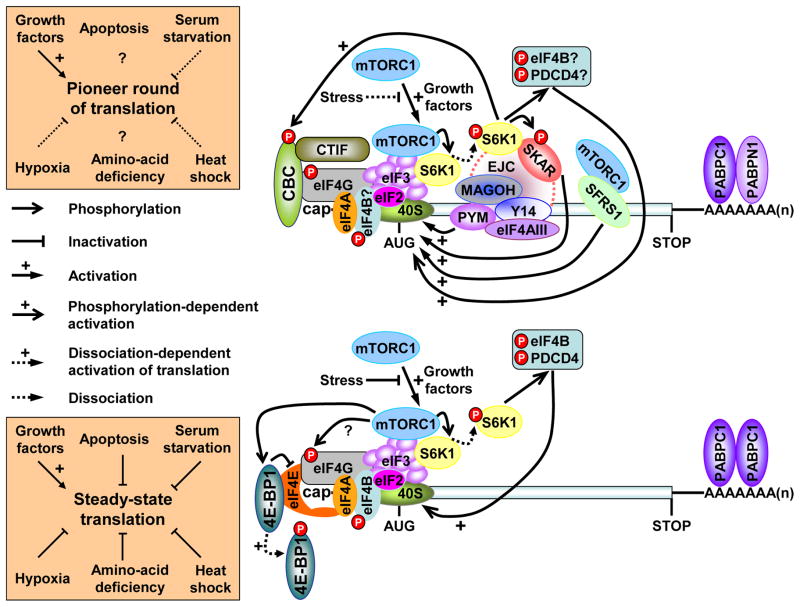
Figure 2. Signaling pathways that regulate the pioneer round of translation and NMD.
The pioneer-round of translation utilizes newly synthesized mRNA bound by the cap-binding protein heterodimer CBP80-CBP20 (CBC) and, provided the mRNA derived from splicing, at least one exon-junction complex (EJC, which consists of but is not limited to MAGOH, Y14, PYM and eIF4AIII) situated ~ 20–24-nucleotides upstream of such a junction. This round of translation (and, thus, NMD for those mRNAs that are NMD targets) is promoted upon activation of the mTORC signaling pathway, i.e, in the absence of stress and the presence of growth factors, by multiple pathways. mTOR-mediated translational activation is best understood for eIF4E-bound mRNAs119. Translational activation, and thus the activation of any associated mRNA decay pathways, involves mTORC1 binding to eIF3, which results in the phosphorylation of the 4E-BP1 translational repressor and consequently the dissociation of inactivated 4E-BP1 from mRNA-bound eIF4E. eIF4G can then interact with and stabilize the binding of eIF4E, eIF4A and PABPC1 to mRNA to ensure efficient translation. mTORC1 binding to eIF3 also results in the phosphorylation of the S6 kinase 1 (S6K1) translational activator and consequently the dissociation of activated S6K1 from mRNA-bound eIF3. Dissociated S6K1 phosphorylates eIF4B and tumor suppressor programmed cell death 4 (PDCD4), which augment scanning of the 43S preinitiation complex to the translation initiation codon. Taking cues from how mTOR activates eIF4E-bound mRNA translation, the mTOR-mediated translational activation of CBC-bound mRNA, and thus the activation of NMD, may also involve mTORC1 binding to eIF3 and the dissociation of activated S6K1 from CBC-bound mRNA. Activated S6K1 is then recruited by the EJC constituent SKAR, which promotes the pioneer round of translation by enhancing the phosphorylation of SKAR and other downstream effectors that may include eIF4B and PDCD4, which associate with not only eIF4E-bound mRNA but also CBC-bound mRNA120. Occurring in parallel, S6K1 phosphorylation by the Cdc42 kinase may augment binding of CBC to mRNA caps, the splicing factor SFRS1 may initiate S6K1 signaling via mTORC1, and the interaction of PYM with the EJC-core proteins Y14 and MAGOH and the 40S ribosomal subunit all appear to promote the pioneer round of translation and, when appropriate, NMD. (After Figure 2 in5.)