Abstract
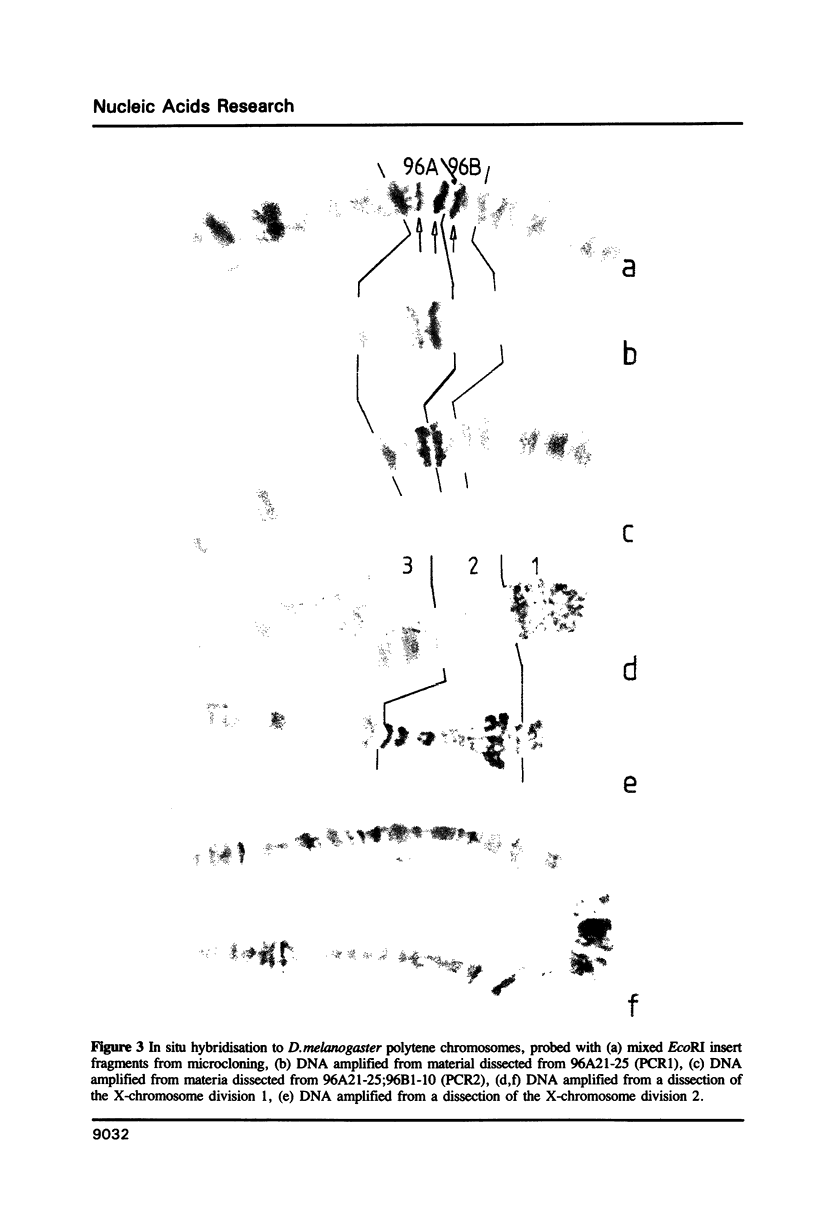
A novel alternative to microcloning for the production of region specific chromosomal DNA is described. In this method, 'microamplification', single bands are dissected from polytene chromosomes and digested with Sau3A. Oligonucleotide adaptors are ligated to these fragments to provide convenient priming sites for polymerase chain reaction amplification. In this way, as much as 1 microgram of DNA can be amplified from a single band. Probes made from PCR amplified DNA from two such dissections have been used to probe cloned DNA form a 100 kb chromosome walk. Whereas conventional microcloning has generated cloned EcoRI fragments corresponding to 3-4 kb of the walk, the PCR probes cover greater than 90% of this chromosomal region. Thus microamplification is significantly more effective than microcloning in providing probes for establishing chromosomal walks.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gough J. A., Murray N. E. Sequence diversity among related genes for recognition of specific targets in DNA molecules. J Mol Biol. 1983 May 5;166(1):1–19. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80047-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horton I. H. A Comparison of the Salivary Gland Chromosomes of Drosophila Melanogaster and D. Simulans. Genetics. 1939 Mar;24(2):234–243. doi: 10.1093/genetics/24.2.234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemeunier F., Ashburner M. A. Relationships within the melanogaster species subgroup of the genus Drosophila (Sophophora). II. Phylogenetic relationships between six species based upon polytene chromosome banding sequences. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1976 May 18;193(1112):275–294. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1976.0046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindsley D. L., Sandler L., Baker B. S., Carpenter A. T., Denell R. E., Hall J. C., Jacobs P. A., Miklos G. L., Davis B. K., Gethmann R. C. Segmental aneuploidy and the genetic gross structure of the Drosophila genome. Genetics. 1972 May;71(1):157–184. doi: 10.1093/genetics/71.1.157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüdecke H. J., Senger G., Claussen U., Horsthemke B. Cloning defined regions of the human genome by microdissection of banded chromosomes and enzymatic amplification. Nature. 1989 Mar 23;338(6213):348–350. doi: 10.1038/338348a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasch E. M., Barr H. J., Rasch R. W. The DNA content of sperm of Drosophila melanogaster. Chromosoma. 1971;33(1):1–18. doi: 10.1007/BF00326379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ripoll P., Pimpinelli S., Valdivia M. M., Avila J. A cell division mutant of Drosophila with a functionally abnormal spindle. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):907–912. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80071-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Röhme D., Fox H., Herrmann B., Frischauf A. M., Edström J. E., Mains P., Silver L. M., Lehrach H. Molecular clones of the mouse t complex derived from microdissected metaphase chromosomes. Cell. 1984 Mar;36(3):783–788. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90358-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scalenghe F., Turco E., Edström J. E., Pirrotta V., Melli M. Microdissection and cloning of DNA from a specific region of Drosophila melanogaster polytene chromosomes. Chromosoma. 1981;82(2):205–216. doi: 10.1007/BF00286105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speek M., Raff J. W., Harrison-Lavoie K., Little P. F., Glover D. M. Smart2, a cosmid vector with a phage lambda origin for both systematic chromosome walking and P-element-mediated gene transfer in Drosophila. Gene. 1988 Apr 15;64(1):173–177. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90491-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urieli-Shoval S., Gruenbaum Y., Sedat J., Razin A. The absence of detectable methylated bases in Drosophila melanogaster DNA. FEBS Lett. 1982 Sep 6;146(1):148–152. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80723-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weith A., Winking H., Brackmann B., Boldyreff B., Traut W. Microclones from a mouse germ line HSR detect amplification and complex rearrangements of DNA sequences. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1295–1300. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02367.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White T. J., Arnheim N., Erlich H. A. The polymerase chain reaction. Trends Genet. 1989 Jun;5(6):185–189. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(89)90073-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




