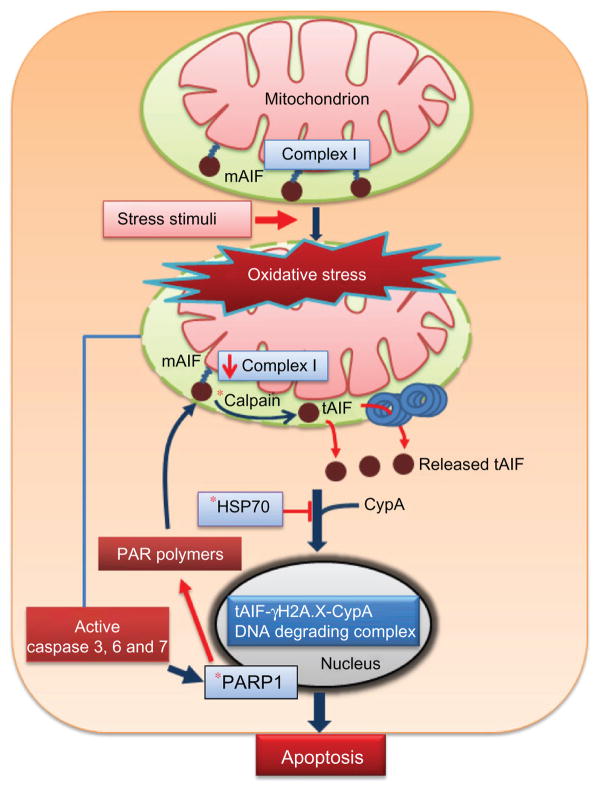
Figure 1.
AIF and intrinsic pathway of apoptosis. Stress stimuli, such as oxidative stress, induce cleavage of mAIF in the mitochondria to tAIF by calpain. Newly formed tAIF escapes from the mitochondria and interacts with cyclophilin A in the cytosol to facilitate translocation into the nucleus. Alternatively, the chaperone, HSP70, can bind tAIF, resulting in sequestration of tAIF in the cytosol and inhibition of AIF-dependent apoptosis. In the nucleus, tAIF forms a DNA degrading complex with phosphorylated histone, γH2A.X, and cyclophilin A to induce DNA fragmentation and apoptosis. AIF release from the mitochondria is also increased by the action of poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 (PARP-1) and PAR polymers.
Note: *Indicates potential target in the AIF pathway for therapeutic intervention.
Abbreviations: AIF, apoptosis-inducing factor; tAIF, truncated apoptosis-inducing factor; HSP, heat shock protein; mAIF, mature apoptosis-inducing factor.