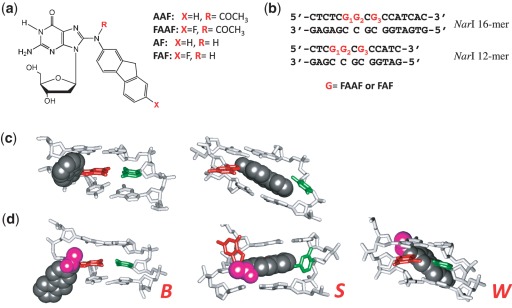
Figure 1.
(a) Chemical structures of AAF, FAAF, AF and FAF adducts; (b) sequences of fully paired 16-mer and 12-mer NarI duplexes used in the present study; major groove views of the central trimer segments of (c) the B/S and (d) B/S/W-conformer equilibrium of FAF and FAAF-modified duplexes. The modified dG and the complementary dC are shown in red and green sticks, respectively, and the aminofluorene moiety is highlighted with shiny gray CPK and the N-acetyl with pink CPK. In the B-type conformer, anti-[FAAF/FAF]dG maintains Watson–Crick hydrogen bonds, thereby placing the carcinogen moiety in the major groove. The carcinogens in the S- and W-conformers stack into the helix or wedged into the minor groove, respectively, with the modified dG in the syn conformation.