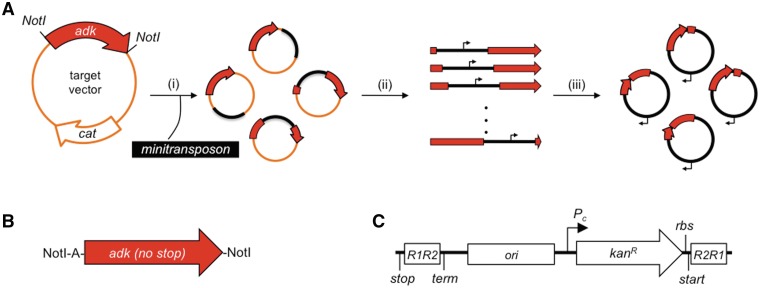
Figure 1.
Scheme for creating PERMUTE libraries. (A) In this method: (i) MuA integrates a synthetic minitransposon (black) into a target vector (orange) containing the adk gene (red), (ii) adk genes harboring an integrated minitransposon are excised from modified target vectors using NotI and (iii) these genes are self-ligated to create a library of vectors that express the different circularly permuted AK variants. (B) The target gene lacks a stop codon and is flanked by identical restriction sites (NotI), which become joined within the circularly permuted genes, where they encode the linker that connects the original N- and C-termini of TnAK. An additional adenine was inserted between the initial NotI site and the adk gene to keep the linker in frame upon permutation. Larger linkers could be incorporated by adding additional codons between the NotI and adenine. (C) The minitransposon contains a stop codon (stop), MuA recognition sites (R1R2 and R2R1), a terminator (term), a pBR322-derived origin of replication (ori), a constitutive promoter (Pc) a kanR selectable marker, a ribosomal binding site (rbs) and a start codon (start).