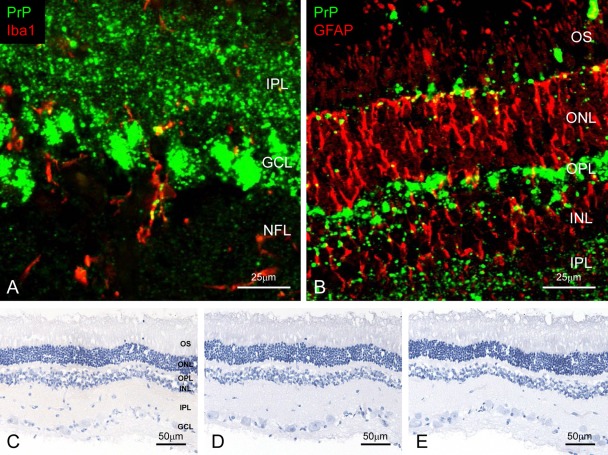
Figure 2.
Detection of disease-associated prion protein (PrPSc) in the retina. Dual immunofluorescence labeled with T1 for PrPSc (green; A and B) and Iba1 (red; A, case 5426) or glial fibrillary acid protein (GFAP; red; B, case 5523). PrPSc accumulates throughout the retina. Granular PrPSc deposits are present in the cytoplasm of the microglia (A) and astrocytes (B). Weak background immunostaining is present with the tyramide signal amplification (TSA) system (C) but not the conventional polymer method (D) in the retina of an uninfected control animal immunolabeled with mAb F99/97.6.1. No specific background immunolabeling is detected in the retina of a control animal immunostained with phosphate-buffered saline instead of the primary prion protein (PrP)–primary antibody using the TSA system (E). NFL, nerve fiber layer; GCL, ganglion cell layer; IPL, inner plexiform layer; INL, inner nucleus layer; OPL, outer plexiform layer; ONL, outer nucleus layer; OS, outer segments.