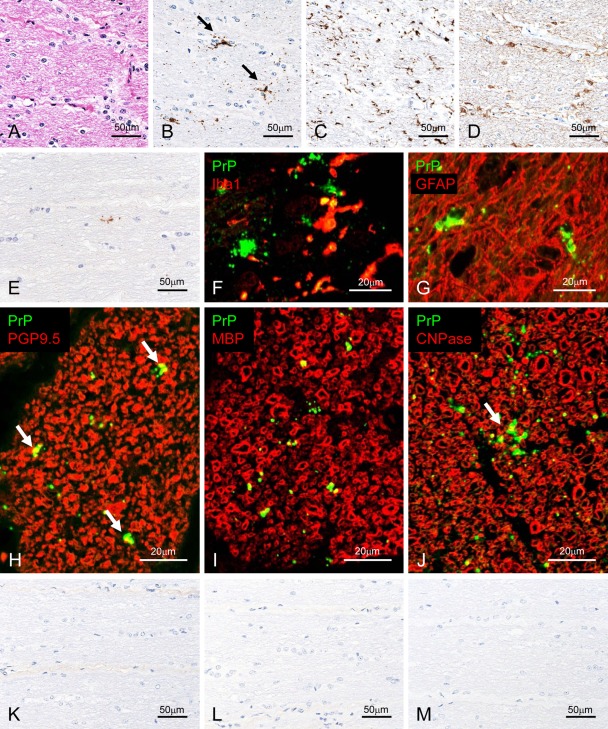
Figure 3.
Detection of disease-associated prion protein (PrPSc) in the optic nerve. Semi-serial sections of experimental bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE) cattle (case 4437) are stained with hematoxylin and eosin (A) and immunolabeled with mAb F99/97.6.1 (B; tyramide signal amplification [TSA] system), Iba1 (C), or glial fibrillary acid protein (GFAP; D). Patchy (arrows in B) and particulate PrPSc deposits are detected in the optic nerve. Weak positive signal was detected in a naturally occurring case (BSE/JP21) with mAb F99/97.6.1 using the TSA system (E). Dual immunofluorescence labeled with mAb T1 (green; F and G) and Iba1 (red; F) or GFAP (red; G) in an experimental BSE animal (case 4612). PrPSc granules are localized in the cytoplasm of microglial cells (F) and astrocytes (G). In addition, periastrocytic deposition of PrPSc is noted (yellow; G). Dual immunofluorescence labeled with F99/97.6.1 (green) and PGP9.5 (red; H) in an experimental BSE animal (case 4437). Peri-axonal localization of PrPSc (arrows) is noted. Dual immunofluorescence labeled with T4 (green; I and J) and MBP (red; I) or CNPase (red; J) in an experimental BSE animal (case 4437). Granular PrPSc is colocalized on the myelin sheath (yellow) and patchy PrPSc (arrow) is located at the periphery of the myelin sheath (yellow). Weak background immunostaining is present in the connective tissue with the TSA system (K) but not the conventional polymer method (L) in the optic nerve of an uninfected control animal immunolabeled with mAb F99/97.6.1. No specific background immunolabeling is detected in the optic nerve of a control animal immunostained with phosphate-buffered saline instead of the primary prion protein (PrP)–primary antibody using the TSA system (M).