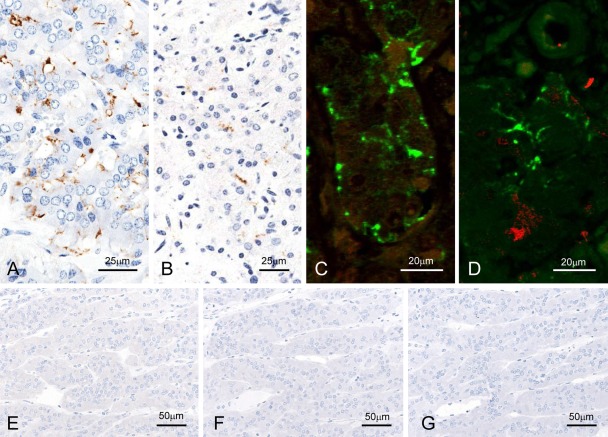
Figure 4.
Detection of disease-associated prion protein (PrPSc) in the adrenal glands. F99/97.6.1mAb-labeled nerve fibers and nerve endings between chromaffin cells of experimental (A, C, and D; case 5087) and naturally occurring (B; BSE/JP17) bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE) cases with the tyramide signal amplification (TSA) method (A and B) and dual immunofluorescence with F99/97.6.1 (green; C and D) and PGP9.5 (N) or S100 (red; O) in case 5087. No background immunostaining is present in the optic nerve of an uninfected control animal immunolabeled with mAb F99/97.6.1 using both TSA (E) and conventional polymer (F) methods. No specific background immunolabeling is detected in the optic nerve of a control animal immunostained with phosphate-buffered saline instead of the primary prion protein (PrP)–primary antibody using the TSA system (M).