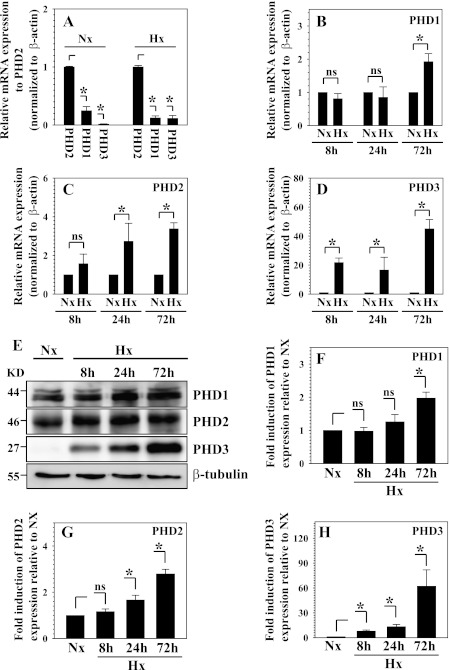
FIGURE 1.
Hypoxic regulation of PHD expression in nucleus pulposus (NP) cells. A, real-time RT-PCR analysis of PHD mRNA expression in NP cells after 72 h of normoxic and hypoxic conditions. Expression of PHD1 and PHD3 is shown relative to PHD2 expression in normoxia or hypoxia, respectively. Note that PHD2 showed the highest relative expression under both normoxia and hypoxia. B, C, and D, real-time RT-PCR analysis of hypoxic change of PHD mRNA expression in NP cells. B, PHD1 mRNA expression was significantly up-regulated at 72 h under hypoxia. ns, not significant. C, the PHD2 expression level was induced significantly by 24 h in hypoxia. D, PHD3 was induced robustly by hypoxia at all time points. E, Western blot analysis of PHDs expression in NP cells cultured under hypoxia. The protein level of all PHDs is induced by hypoxia. PHD3 shows a robust response to hypoxia, whereas the PHD1 response was not as pronounced. KD, kilodalton. F, G, and H, multiple blots were quantified by densitometric analysis. β-tubulin expression was used as a loading control and to calculate relative expression level in hypoxia compared with normoxic level. PHD3 showed the most striking hypoxic induction as early as 8 h. The PHD2 protein level was also significantly increased at 24 h. PHD1 showed induction only at 72 h. Data are represented as mean ± S.E. of three independent experiments performed in triplicate (n = 3). *, p < 0.05.