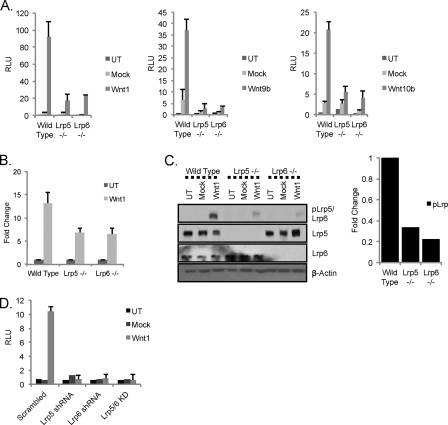
FIGURE 3.
LRP5 and LRP6 are both required for efficient signaling in response to Wnt1. A, absence of either LRP5 or LRP6 results in loss of canonical Wnt activity in response to Wnt1. Wild type, lrp5−/−, and lrp6−/− MEFs were transfected with the Wnt reporter superTOP-FLASH (and Renilla luciferase) along with plasmids encoding mWnt1 or mWnt10b (left- and right-hand side, respectively) (or without the ligand expression plasmids; mock) or with ectopic addition of rmWnt9b (400 ng/ml; middle panel). Cells were processed as described for Fig. 2A. B, Wnt1-dependent transcriptional activation of Axin2. Wild type, lrp5−/−, and lrp6−/− MEFs were plated, transfected with mWnt1 plasmid, and processed for analysis of Axin2 mRNA levels (as per Fig. 2B). C, Wnt1-mediated proximal canonical Wnt signaling. Wild type, lrp5−/−, and lrp6−/− MEFs were transduced with lentiviral constructs expressing Wnt1 or the vector backbone (Mock) or untransduced (UT). 36 h later, proteins were analyzed by Western blotting as described for Fig. 2C. Relative phospho-LRP activation was quantified (right-hand side). D, Wnt1 signaling in MEFs following shRNA-mediated knockdown of lrp5 or lrp6. Wild type MEFs were transduced with lentiviral shRNA constructs targeting lrp5, lrp6, or both mRNAs. 24 h later, cells were transfected with TOP-FLASH, Renilla luciferase, and mWnt1 expression construct and processed as for Fig. 2D. RLU, relative luminescence units; KD, knockdown. Error bars show standard deviations.