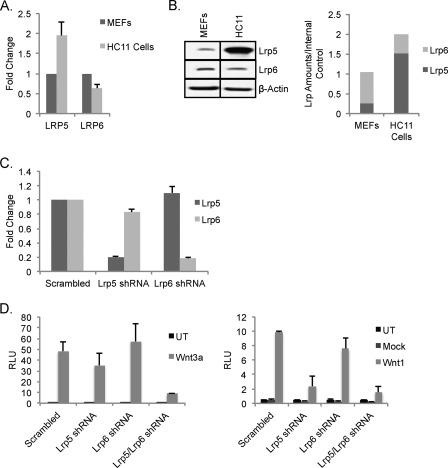
FIGURE 5.
Mammary epithelial cells with endogenously high expression levels of LRP5 compared with MEFs do not require LRP6 for Wnt1-responsiveness. A, evaluation of LRP expression patterns in HC11 cells. The relative mRNA expression of LRP5 and LRP6 was compared for MEFs and HC11 cells using qRT-PCR analysis (normalized to housekeeping genes YWHAZ and hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase). B, relative LRP expression in HC11 cells. Wild type MEFs and HC11 cells were harvested and analyzed for their LRP expression (using β-actin as a loading control) as for Fig. 1. C, RNAi-mediated knockdown of LRP5 and LRP6. HC11 cells were transduced with lentiviral shRNA constructs targeting lrp5, lrp6, or a scrambled control (as for Fig. 2E). qRT-PCR analysis shows the specificity and efficiency of the shRNA constructs. D, evaluation of the requirement for LRP5 and/or LRP6 in response to Wnt3a and Wnt1 in HC11 cells. Knockdown cells (prepared as for C) were transfected with superTOP-FLASH, Renilla luciferase, and either mWnt3a or mWnt3a (D). Cells were lysed 36 h post-transfection, and superTOP-FLASH reporter activity was measured using a luciferase assay. Results are shown from triplicate wells and are representative of three independent experiments. UT, untransduced; RLU, relative luminescence units. Error bars show standard deviations.