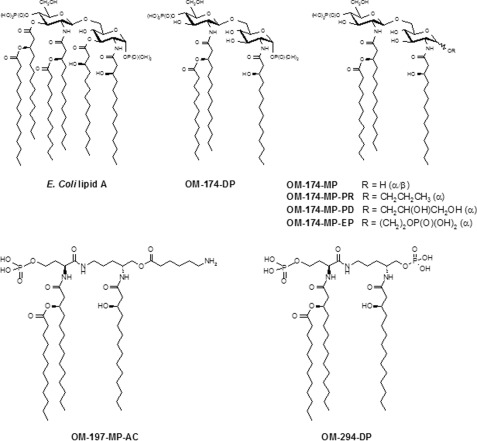
FIGURE 1.
Molecular structure of triacylated lipid A analogs. E. coli lipid A characterized by a diglucosamine backbone, six acyl chains, and two phosphate groups. The triacylated compound OM-174-DP is a fully synthetic molecule that was originally produced by deacylation of three of the six acyl chains of E. coli lipid A, maintaining the diglucosamine backbone of lipid A. OM-174-MP, OM-174-MP-PD, OM-174-MP-EP, and OM-174-MP-PR were derivatives of OM-174-DP obtained by chemical synthesis where the anomeric phosphate group was substituted by the following residues (R): hydrogen (MP), PD, EP, or PR. OM-294-DP is a completely synthetic triacylated molecule where the diglucosamine backbone has been replaced by a pseudodipeptide moiety plus the two phosphate groups (11). OM-197-MP-AC is also a triacylated synthetic molecule with a pseudodipeptide backbone identical to OM-294-DP with the substitution of the second phosphate group by an aminocaproyl (AC) residue.