Figure 1.
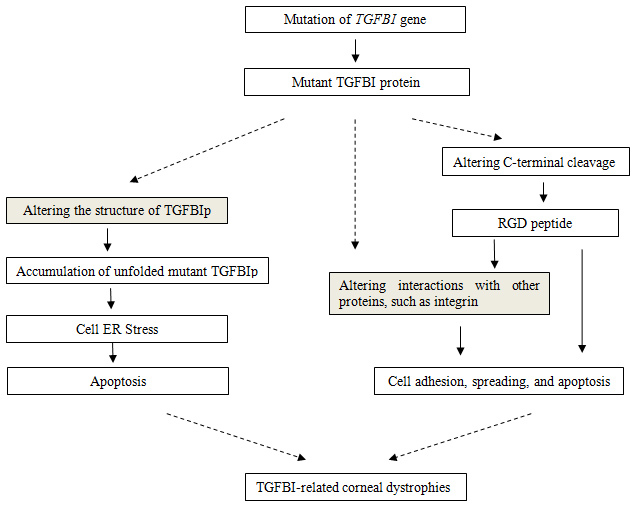
Schematic of proposed mechanism of TGFBI-related corneal dystrophies in present study. The hypothesis of pathogenesis of TGFBI-related corneal dystrophies mainly consists of two aspects: altering the binding interactions of TGFBIp with other critical proteins and interfering with the TGFBIp folding. The influence of TGFBI mutations on C-terminal cleavage and cell endoplasmic reticulum stress investigated in the present study was based on the aspects of the hypothesis. The mechanism by which these mutations cause disease remains unknown, as indicated by the dashed arrow.
