Fig. 1.
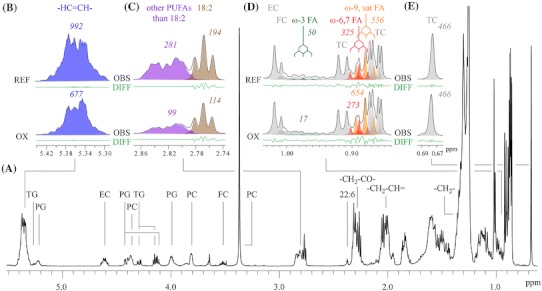
A 1H NMR spectrum of extracted serum with signal assignments (a). Some essential parts of the spectra (b–e) before and after the oxidation are shown at the top of the figure. The signals arising from the double bond protons (b) and the bisallylic protons from PUFAs (c) decrease during oxidation. There are also changes in the amounts of different fatty acids (d). Cholesterol oxidizes slightly under the conditions used and these oxysterol C(18)H3 signals resonate at 0.61–0.69 ppm. The signal areas are referenced to total cholesterol C(18)H3 signals including also the oxidized forms (e). EC esterified cholesterol, FA fatty acid, FC free cholesterol, PC phosphatidylcholine, PG phosphoglyceride, sat saturated, TC total cholesterol, TG triglyceride
