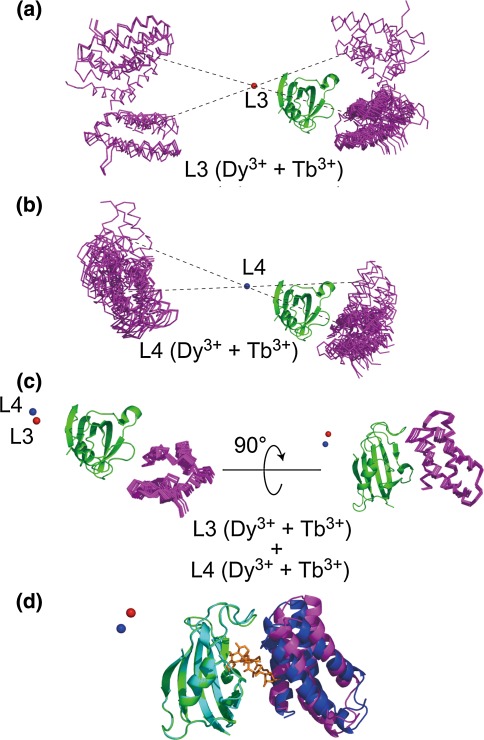
Fig. 3.
The PCS-based docking structure between the FKBP12-rapamycin and FRB domains. Since PCS data were not obtained for rapamycin, rapamycin was omitted during the structure calculation. a Calculated FKBP12-FRB complex structure based on PCS data from L3-FKBP12 using two metals, both Dy3+ and Tb3+. b Calculated FKBP12-FRB complex structure based on PCS data from L4-FKBP12 using two metals, both Dy3+ and Tb3+. c Calculated FKBP12-FRB complex structure based on PCS data from both L3- and L4-FKBP12 using two metals, both Dy3+ and Tb3+. Through (a) to (c), obtained structures were superimposed on FKBP12 moiety. In (a), (b) and (c), metal positions are shown in ball (red for L3 and blue for L4), FKBP12 in green ribbon and FRB in magenta stick. d Ribbon representation of the PCS-based structure (green for FKBP12 and magenta for FRB) and the crystal structure of FKBP12/rapamycin/FRB ternary complex (Liang et al. 1999, 1fap.pdb; cyan ribbon for FKBP12, orange stick for rapamycin and blue ribbon for FRB). The lowest energy structure of the PCS-based structure of the FKBP12-FRB complex was superimposed on FKBP12 moiety of the crystal structure of the ternary complex (Liang et al. 1999, 1fap.pdb). The main chain atom RMSD of the FKBP12 moiety in the binary and the ternary complexes was estimated to be 0.5 Å. The main chain atom RMSD of the FRB moiety in the ternary complex of the crystal structure and the PCS-based NMR structure was estimated to be 2.9 Å