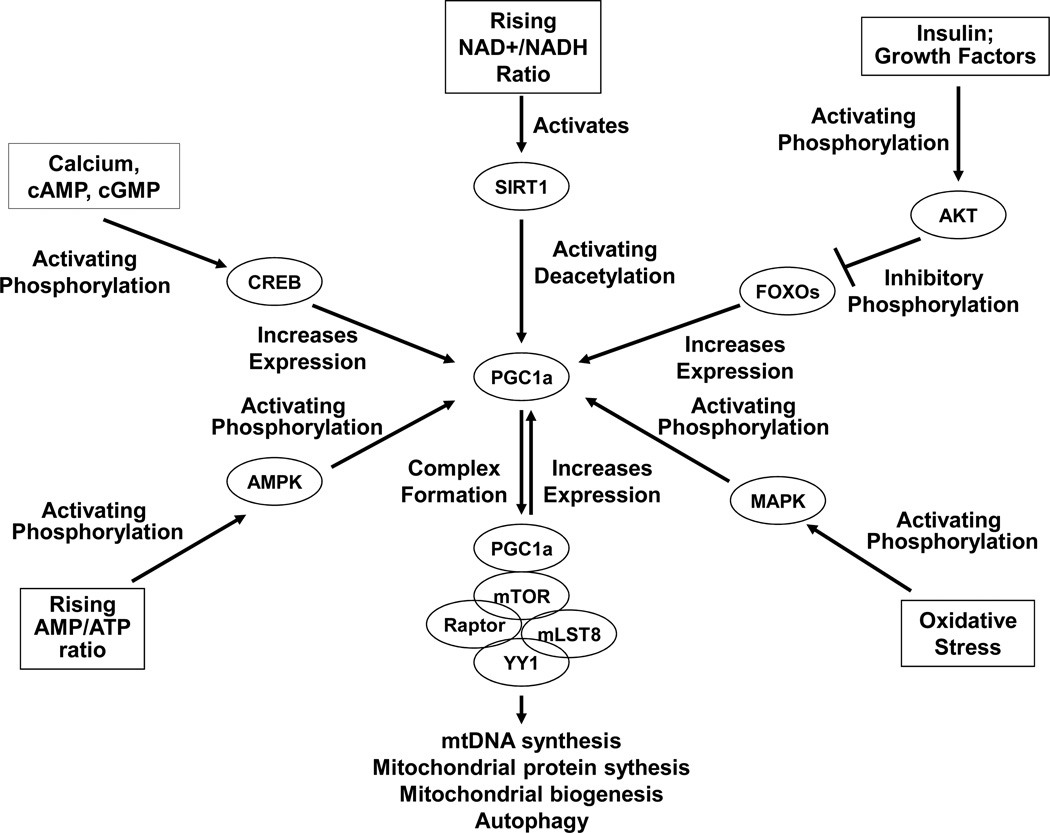
Figure 4. PGC1a, a key regulator of mitochondrial biogenesis, is regulated by various nutrient, energy, and stress-sensing pathways.
This diagram presents a schematic summary of different proteins and transcription factors that regulate PGC1a activity and levels. It is very simplified, and as more is learned about mitochondrial biogenesis the indicated relationships may change. Briefly, SIRT1-mediated PGC1a deacetylation and MAPK-mediated PGC1a phosphorylation induce PGC1a activation. AMPK also activates PGC1a through a direct phosphorylation event or indirectly through intermediates. The CREB transcription factor activates PGC1a expression. A FOXO transcription factor, FKHR, also appears to activate PGC1a expression; by retaining FOXOs in the cytosol, AKT phosphorylation of FOXOs would prevent this contribution. Activated PGC1a reportedly forms a super-complex with the mTOR-containing TORC1 complex (mTOR, raptor, and mLST8) and the YY1 transcription factor. This activated super-complex expresses genes needed to replicate mtDNA, produce mitochondrial proteins, accomplish mitochondrial biogenesis, and support autophagy. It also leads to the production of more PGC1a.