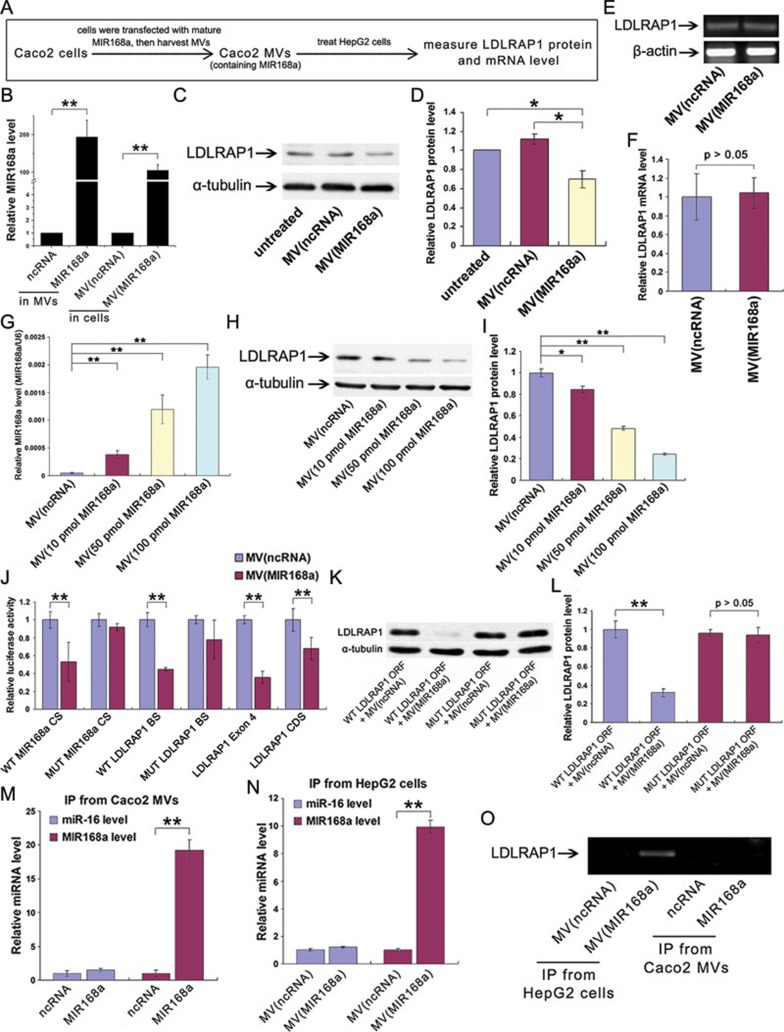
Figure 4.
AGO2-associated mature MIR168a in Caco-2 cell-derived MVs sufficiently reduces mammalian LDLRAP1 protein level in recipient HepG2 cells. (A) A flow chart of the experimental design. (B) The elevation of MIR168a in Caco-2 MVs after transfection with mature MIR168a (left) and in HepG2 cells after treatment with Caco-2 MVs (right; n = 9). Caco-2 MVs were harvested after transfecting the cells with mature MIR168a or ncRNA. (C) Western blot analysis of LDLRAP1 protein levels in HepG2 cells treated with or without Caco-2 MVs. Caco-2 MVs were harvested after transfecting the cells with mature MIR168a or ncRNA. (D) The quantification of the LDLRAP1 protein expression in C (n = 6). (E, F) Semi-quantitative RT-PCR (E) and qRT-PCR (F) analysis of the LDLRAP1 mRNA levels in HepG2 cells treated with or without Caco-2 MVs (n = 5). (G, H) The levels of MIR168a (G) and LDLRAP1 protein (H) in HepG2 cells treated with Caco-2 MVs derived from Caco-2 cells transfected with different doses (10, 50, or 100 pmol/105 cells) of mature MIR168a or ncRNA. (I) The quantification of the LDLRAP1 level in H (n = 3). (J) The luciferase activities in luciferase reporter-transfected HepG2 cells treated with or without Caco-2 MVs (n = 9). (K) LDLRAP1 protein level in 293T cells transfected with WT or MUT LDLRAP1 ORF and then treated with Caco-2 MVs. (L) The quantification of the LDLRAP1 protein expression in K (n = 3). (M, N) The association of MIR168a with AGO2 in Caco-2 MVs (M) and HepG2 cells treated with Caco-2 MVs (N). The levels of MIR168a and miR-16 (control) in anti-AGO2 immunoprecipitated products detected by qRT-PCR (n = 9). (O) The association of LDLRAP1 mRNA with AGO2 in Caco-2 MV-treated HepG2 cells or Caco-2 MVs. The LDLRAP1 mRNA in anti-AGO2 immunoprecipitated products from HepG2 cells (lanes 1 and 2) and Caco-2 MVs (lanes 3 and 4) was detected by semi-quantitative RT-PCR with 25-30 cycles. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01.