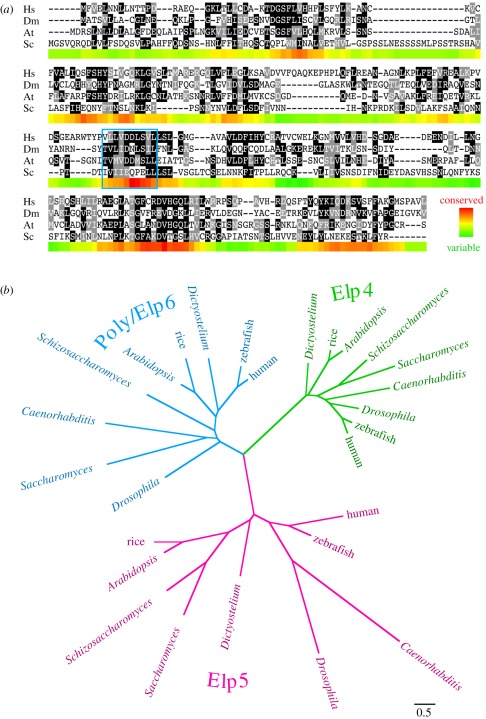
Figure 2.
Alignment and phylogenetic analysis of Poly. (a) Alignment showing Poly homologues in human (Hs; NP_001026873), Drosophila melanogaster (Dm; AAF40432), Arabidopsis thaliana (At; NP_567351) and Saccharomyces cerevisiae (Sc; NP_014043), with shading of identical and similar amino acids as rendered by the BOXSHADE program. The coloured band underneath each section of the alignment indicates sequence conservation according to the PAM250 matrix, averaged over a sliding window of 10 amino acids. The location of the Walker B motif (ordinarily associated with ATP binding) is indicated by a blue box, although no Walker A (P-loop) motif required for ATP hydrolysis is similarly conserved. (b) Phylogenetic tree showing the relationship between Poly, identified as the Drosophila orthologue of Elp6, and homologous sequences. The scale bar indicates distance according to the WAG substitution matrix.