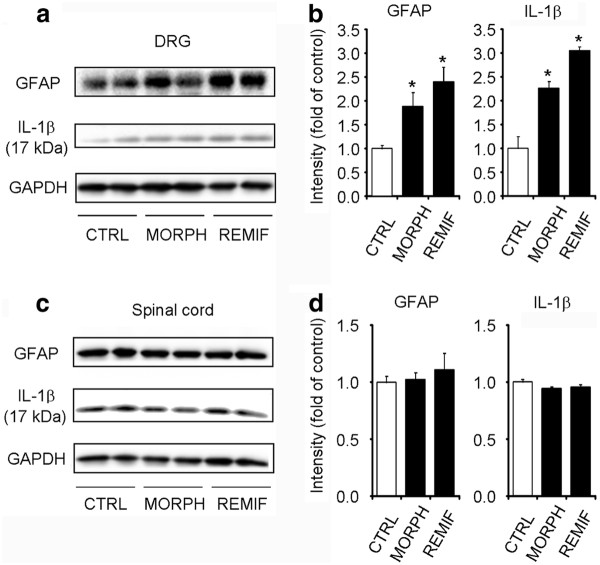
Figure 6.
Intrathecal injection of morphine and remifentanil increases GFAP expression and IL-1β activation in DRGs but not in spinal cords. (A) Western blotting showing the expression of GFAP and IL-1β (17 kDa cleaved form) in DRGs after intrathecal injection of morphine (10 nmol, 2 h) and remifentanil (1 nmol, 2 h). (B) Quantification of GFAP and IL1β (17 kDa) bands in DRGs. *P < 0.05, compared to saline control; ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post hoc test, n = 4 mice. (C) Western blotting showing the expression of GFAP and IL-1β (17 kDa) in spinal cord dorsal horns after intrathecal injection of morphine (10 nmol, 2 h) and remifentanil (1 nmol, 2 h). (D) Quantification of GFAP and IL-1β bands in spinal cord dorsal horns. Note there is no change in spinal GFAP expression and IL-1β activation after morphine treatment. *P < 0.05, compared to saline control; ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post hoc test, n = 4 mice. CTRL, vehicle control; MORPH, morphine; REMIF, remifentanil.