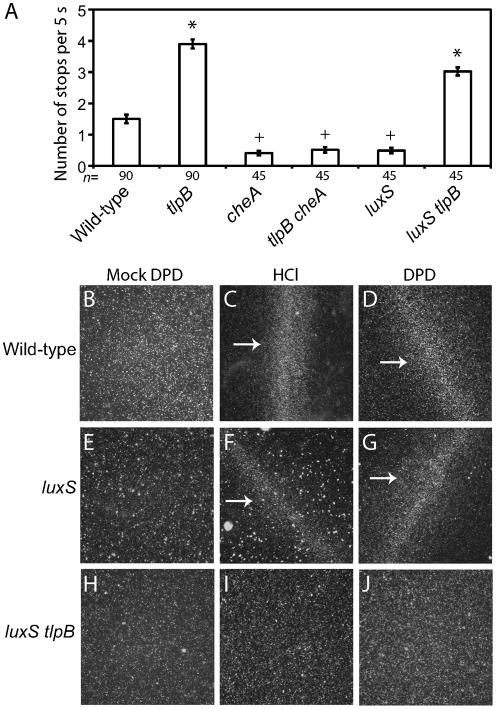
Fig. 4.
tlpB functions in a signalling pathway downstream of luxS and upstream of cheA. (A) Swimming behaviours in BB10 of G27 wild-type, tlpB, cheA, tlpB cheA, luxS and luxS tlpB isogenic strains were observed by video microscopy, and the number of stops that individual bacteria performed during 5 s was recorded. The number of individual bacterial cells scored (n) for each strain is indicated below the column; bars indicate se. Symbols (*, +) indicate strains that are statistically indistinguishable from each other (P>0.001 with Bonferroni correction). (B–J) The wet-mount chemotaxis assay was used to analyse chemotatic behaviour of the indicated isogenic mutant strains in response to mock DPD, the known chemorepellent 0.1 M HCl and 0.1 mM synthetic DPD. White arrows indicate bacterial barrier formation.